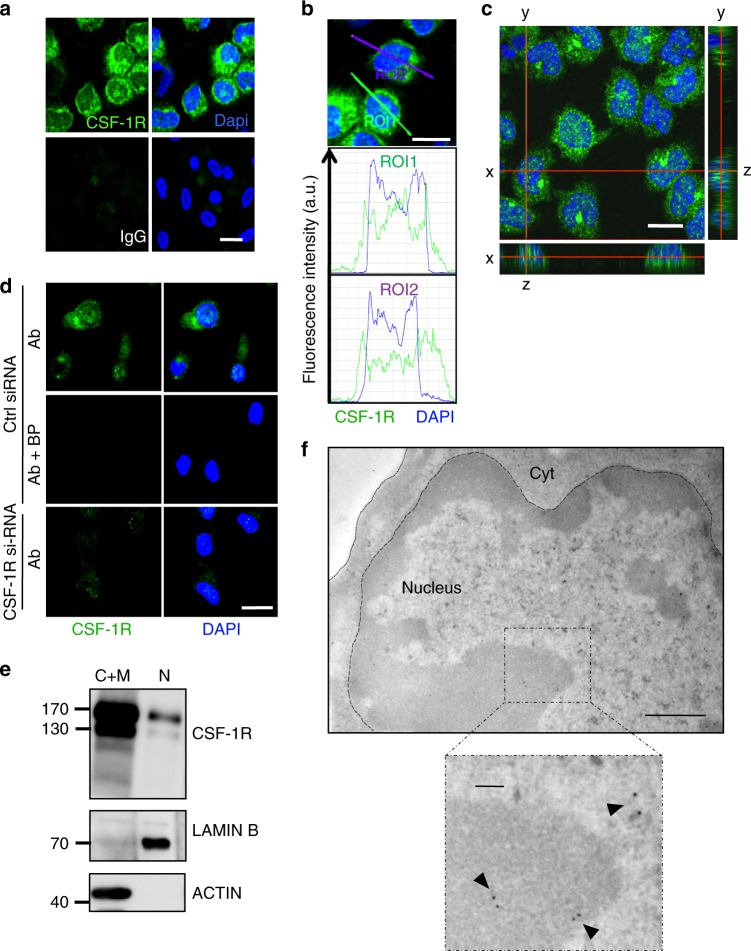
Fig. 1.
A fraction of CSF-1R is located in the nucleus of human monocytes. a Sorted peripheral blood human monocytes were stained with an anti-CSF-1R antibody (Cter sc-692) or a control IgG (green) and Dapi (blue), followed by confocal imaging analysis (n = 3, scale: 10 μm). b Quantification of the signal generated by CSF-1R labeling (green) and Dapi (blue) according to indicated axes (A.U.: arbitrary units, ROI: region of interest, scale: 10 μm). c Monocytes were stained with an anti-CSF-1R antibody (Cter sc-692) and Dapi (blue), followed by confocal imaging analysis (stack of 50 pictures of 0.2 μm) to reconstitute an orthogonal view (scale: 10 μm). d The specificity of CSF-1R labeling with sc-692 antibody (Ab in green) was explored in monocytes transfected 24 h before with a CSF-1R specific or a control si-RNA and treated or not with sc-692 blocking peptide (BP, n = 2, scale: 10 μm, Dapi in blue). e Monocytes were fractionated into cytoplasmic plus membrane (C+M) and nuclear (N) fractions and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies that recognize CSF-1R (Cell signaling #3152), Lamin B (N fraction) and actin (C+M fraction) (n = 3). f Immunogold analysis of CSF-1R expression in monocytes using the anti-Cter sc-692 antibody and electron microscopy (n = 2, scale: 500 nm; insert: 100 nm)