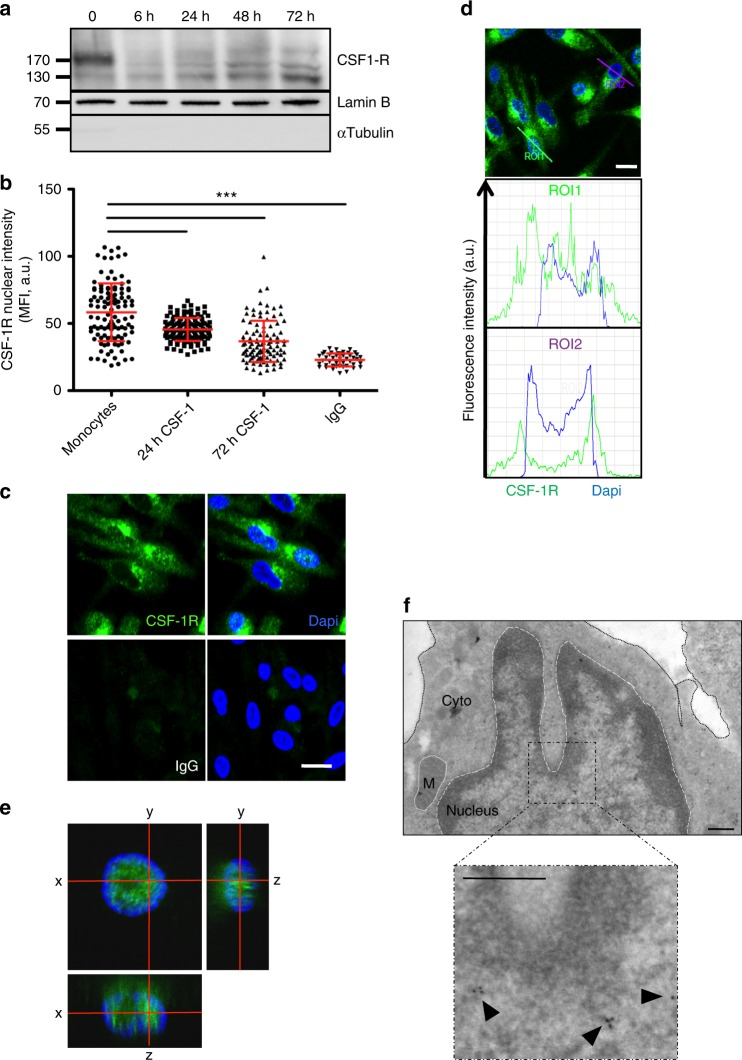
Fig. 6.
Differential CSF-1R chromatin localization in CSF-1-induced macrophages. a Nuclear proteins were extracted from monocytes stimulated with 100 ng/mL CSF-1 during the indicated times, and analyzed by immunoblotting for CSF-1R, Lamin B (nucleus marker) and α-tubulin (cytosol marker) (n = 3). b Monocytes were stimulated or not with 100 ng/mL CSF-1 during the indicated times, stained with an anti-CSF-1R antibody (Cter sc-692) or a control IgG and Dapi, followed by confocal imaging analysis of CSF-1R nuclear localization (MFI, mean fluorescence intensity, A.U. arbitrary units, mean +/− SD, Paired t test: ***P < 0.001, n = 1). c Monocytes were treated 3 days with 100 ng/mL CSF-1, fixed and stained for CSF-1R or control IgG (green) and Dapi (blue) followed by confocal imaging (n = 3, scale: 10 μm). d Quantification of the signal generated by CSF-1R labeling (green) and Dapi labeling (blue) according to indicated axes (A.U.: arbitrary units, ROI: region of interest, scale: 10 μm). e Macrophages were stained with an anti-CSF-1R antibody (C-ter sc-692) and Dapi (blue), followed by confocal imaging analysis (stack of 50 pictures of 0.2 μm) to reconstitute an orthogonal view (scale: 10 μm). f Monocytes were differentiated 3 days with 100 ng/mL CSF-1, fixed and stained for CSF-1R (sc-692) followed by electron microscopy (n = 1, scale: 500 nm)