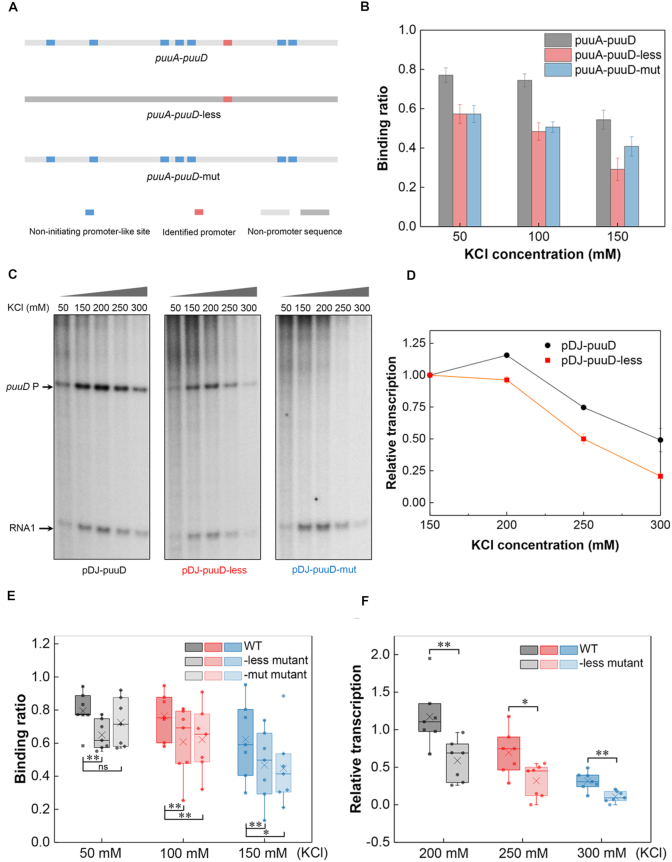
Figure 7.
The non-initiating promoter-like sites contribute to RNAP binding and transcription. (A) Schematic of the identified promoter and promoter-like sites in puuA-puuD and two derived constructs. (B) RNAP binding to puuA-puuD, puuA-puuD-less and puuA-puuD-mut at varying KCl concentrations. Three independent EMSA experiments were used for the analysis. (C) Effects of KCl concentration on puuD transcription from plasmids pDJ-puuD, pDJ-puuD-less and pDJ-puuD-mut. KCl concentration used in each lane is shown on the top. Arrows indicate the transcripts from puuD promoter and internal control RNA1. (D) Relative quantification of the transcripts from pDJ-puuD and pDJ-puuD-less with increasing KCl. The puuD signal at 150 mM KCl was set as 1. RNA1 was used to normalize the signal. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (E) RNAP binding to the wild-type intergenic regions, -less mutants and -mut mutants at 50 mM KCl, 100 mM KCl and 150 mM KCl. -less mutant, all the non-initiating promoter-like sites were removed; -mut mutant, only the actively initiating promoter was mutated. (F) Transcription from the wild-type intergenic regions and -less mutants with increasing KCl concentrations relative to 150 mM KCl. **P ≤ 0.01; *P ≤ 0.05; ns, P > 0.05; two-sided t-test.