Figure 1.
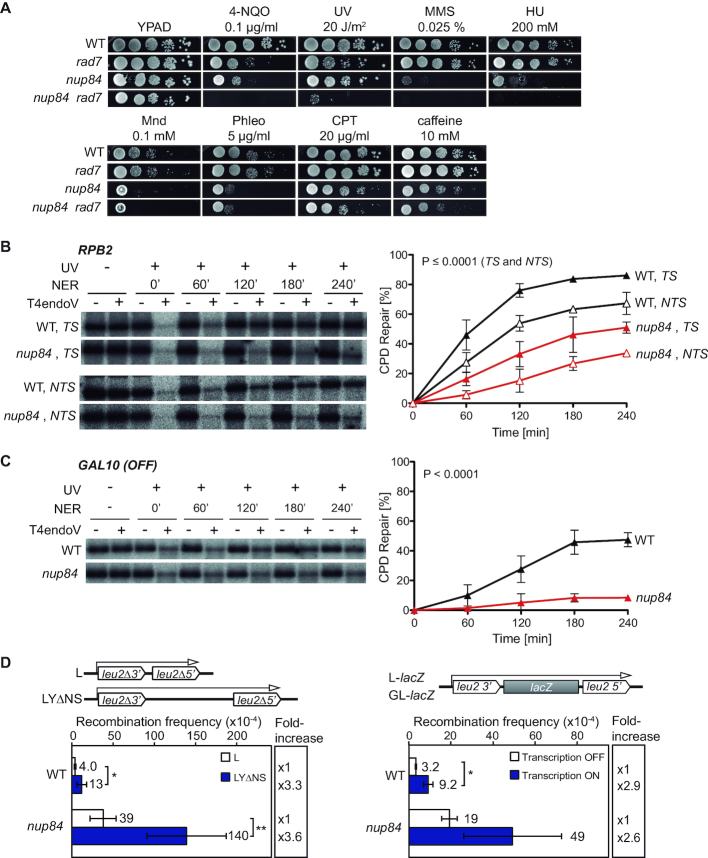
Nup84 is required for the repair of DNA damage. (A) Sensitivity of wild-type (WT, BY4741), rad7Δ (yHG72-1B), nup84Δ (YDL116W) and nup84Δ rad7Δ (yN84R7-24A) cells to 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO), UV light, methyl methanesulfonate (MMS), hydroxyurea (HU), menadione (Mnd), phleomycin (Phleo), camptothecin (CPT) and caffeine. 10-fold serial dilutions of exponentially growing cells are shown. (B) Representative results of Southern analysis showing the repair of a 4.4-kb (NsiI/PvuI) RPB2 fragment in WT (BY4741) and nup84Δ (YDL116W) cells on the transcribed strand (TS) and the non-transcribed strand (NTS) (left). Non-irradiated DNA and DNA not treated with T4endoV were used as controls. Graphical representation of the quantified results is shown (right). Average values and standard deviations of independent experiments are plotted (N ≥ 3). P values are shown (two-way ANOVA). The initial damage generated was on average 0.51 CPD/kb in the TS and 0.56 CPD/kb in the NTS. (C) Representative results of Southern analysis showing the repair of a 1.6-kb (EcoRI/SalI) GAL10 fragment in WT (BY4741) and nup84Δ (YDL116W) cells (left). Analysis was performed on the TS in conditions in which GAL10 was not transcribed (glucose). The initial damage was 0.54 CPD/kb on average. Other details as in B. (D) Recombination analysis in WT (WRB1-1A) and nup84Δ (WRN84B1α-3D) cells carrying the L and LYΔNS plasmid systems (left) or the L-lacZ (Transcription ON) and GL-lacZ (Transcription OFF) systems grown in glucose-containing medium (right). Average and standard deviation of fluctuation tests consisting in the median value of six independent colonies each one are shown (N ≥ 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (unpaired Student's t-test). A scheme of the system is shown on top of each panel.