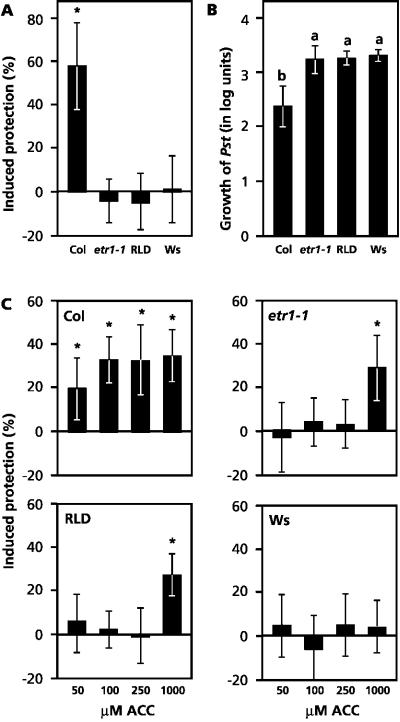
Figure 6.
Level of WCS417r-induced protection, basal resistance, and ACC-induced protection against Pst in Col, etr1-1, RLD, and Ws. A, Quantification of WCS417r-mediated ISR. ISR was triggered by growing plants in soil containing ISR-inducing P. fluorescens WCS417r bacteria at 5 × 107 cfu g−1. Five-week-old plants were challenge-inoculated with a bacterial suspension of virulent Pst at 2.5 × 107 cfu mL−1. Three days after challenge inoculation the percentage of diseased leaves was assessed and the level of induced protection was calculated. Induced protection is presented as a reduction of disease symptoms relative to challenged control plants. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared with noninduced control plants (Student's t test; α = 0.05; n = 20–25). Data presented are means (±sd) from representative experiments that were performed at least twice with similar results. B, Proliferation of Pst over a 3-d time interval. Five-week-old plants were infected by pressure infiltrating a suspension of virulent Pst at 5 × 105 cfu mL−1 into the leaves. Immediately after pressure infiltration and 3 d later, the number of Pst bacteria per gram of leaf fresh weight was determined and the proliferation over a 3-d time interval was calculated. Data presented are the means (±sd) of the proliferation values (log cfu g−1) of a representative experiment that was repeated twice with similar results. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences between genotypes (Fisher's lsd test; α = 0.05; n = 6). C, Quantification of ACC-induced protection against Pst. Plants were dipped in a solution containing different concentrations of ACC 3 d before challenge inoculation with Pst. Three days after challenge, the level of induced protection was assessed as described above.