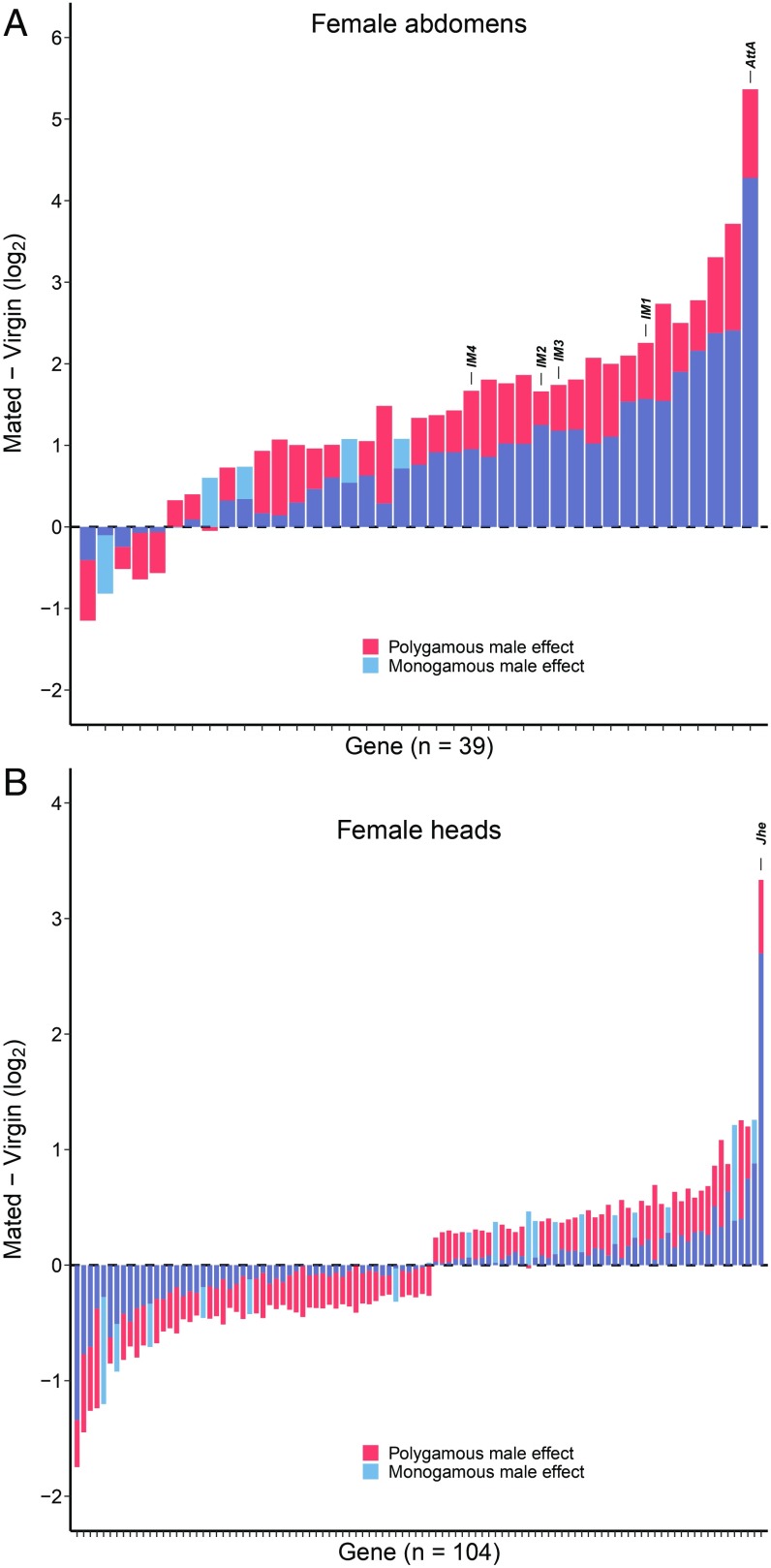
Fig. 2.
Change in gene expression 24 h after mating (log2 mated–log2 virgin) in the female abdomen (A) and female head (B) for mating-responsive genes that are significantly differentially affected by polygamous versus monogamous male mates. Genes encoding immune-induced peptides (A) and Juvenile hormone esterase (B) are labeled. In both female abdomens and heads, monogamous males elicit a weaker transcriptional response.