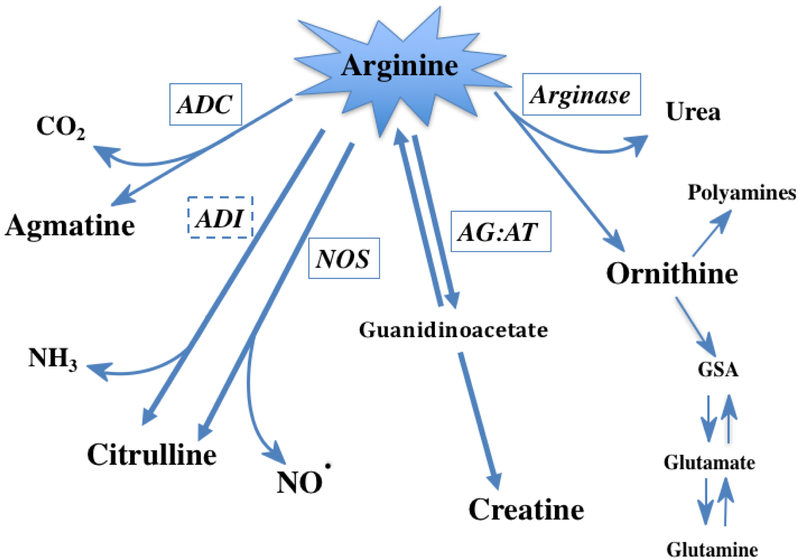
Figure 1. Metabolic Fates of Arginine.
Arginine can be degraded by a number of enzymes within the cell. Of the five enzymes pictured, four are expressed in humans while arginine deiminase (ADI) has only been described in non-mammalian organisms/bacteria. Arginine decarboxylase (ADC) has been detected in neural tissue and degrades arginine to carbon dioxide and agmatine. ADI and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) both produce citrulline and either ammonia or nitric oxide, respectively. Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AG:AT) is important for synthesis of creatine. Arginase, the final enzyme of the urea cycle, produces urea as well as ornithine that can re-enter the urea cycle or be used by another set of enzymes for the production of polyamines or converted to other amino acids. Note: all of the enzymes pictured above except for ADI (dashed box) are expressed in humans (solid boxes).