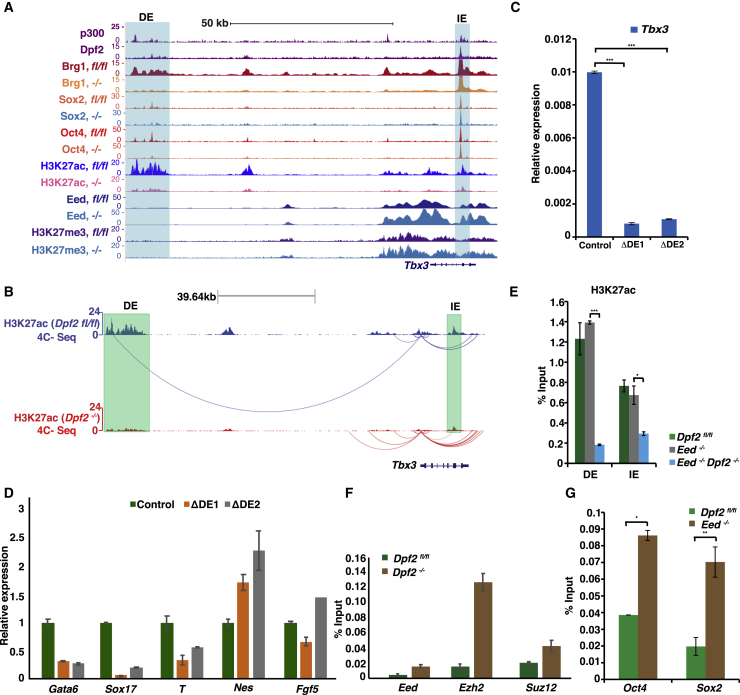
Figure 6.
Dpf2 and Eed Regulate Tbx3 Expression by Controlling Histone Modifications and Accessibility of Pluripotency TFs at Different Enhancers
(A) Genome browser view of ChIP-seq tracks for DPF2 and P300 in WT ESCs and BRG1, OCT4, SOX2, EED, H3K27ac, and H3K27me3 in Dpf2fl/fl and Dpf2−/− ESCs (indicated as fl/fl and −/−) at the Tbx3 locus. The distal enhancer (DE) and intronic enhancer (IE) enhancers are highlighted. The values on the y axis represent fold enrichment over control.
(B) Circular chromatin conformation capture (4C-seq) analysis of the Tbx3 promoter. The arcs represent significant interactions from the Tbx3 promoter viewpoint in Dpf2fl/fl and Dpf2−/− ESCs. The DE and IE are indicated.
(C) Transcript levels of Tbx3 in two DE KO ESC clones and control ESCs based on qPCR.
(D) As in (C), except for the indicated lineage markers in day 6 EBs from WT and the two DE KO ESCs.
(E) H3K27ac levels at Tbx3 enhancers in Dpf2fl/fl, Eed−/−, and Eed/Dpf2 double KO ESCs, determined by ChIP-qPCR.
(F) As in (E), except for relative levels of EED, EZH2, and SUZ12 at the IE of the Tbx3 gene in Dpf2fl/fl and Dpf2−/− ESCs.
(G) As in (E), except for relative levels of OCT4 and SOX2 at the IE of the Tbx3 gene in WT and Eed−/− ESCs.