Figure 8. Hypothesized mechanism of action by GCN5L1 in cardiac cells following I/R injury.
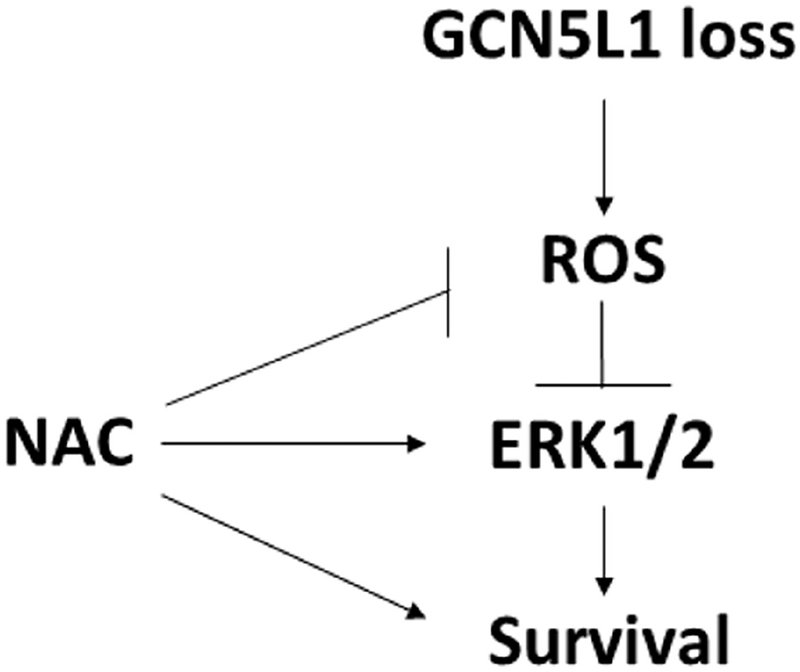
Loss of GCN5L1 disrupts mitochondrial function leading to increased ROS production. Treatment of cells with antioxidants rescues GCN5L1-deficient cells after ischemic injury.
