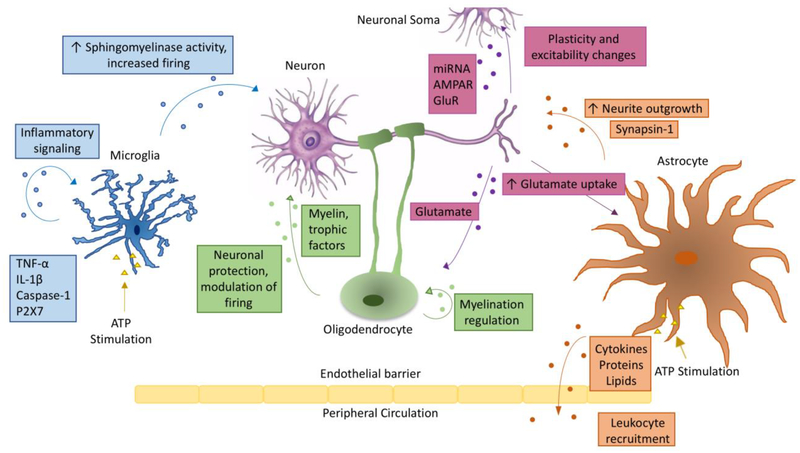
Figure 1: Extracellular vesicle crosstalk within the CNS.
Schematic representation of extracellular vesicle transfer between different cell types within the central nervous system. Arrows indicate the direction of transfer, and are labeled with the contents of EVs commonly found for that cell-to-cell communication pathway and with some of the functional roles identified for the pathway. EVs can transfer contents between various pairs among the cell types depicted in the figure, i.e. neurons, microglia, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. See text for complete details. ATP stimulation is included for microglia and astrocytes, whose cargo is modulated depending on activation state.