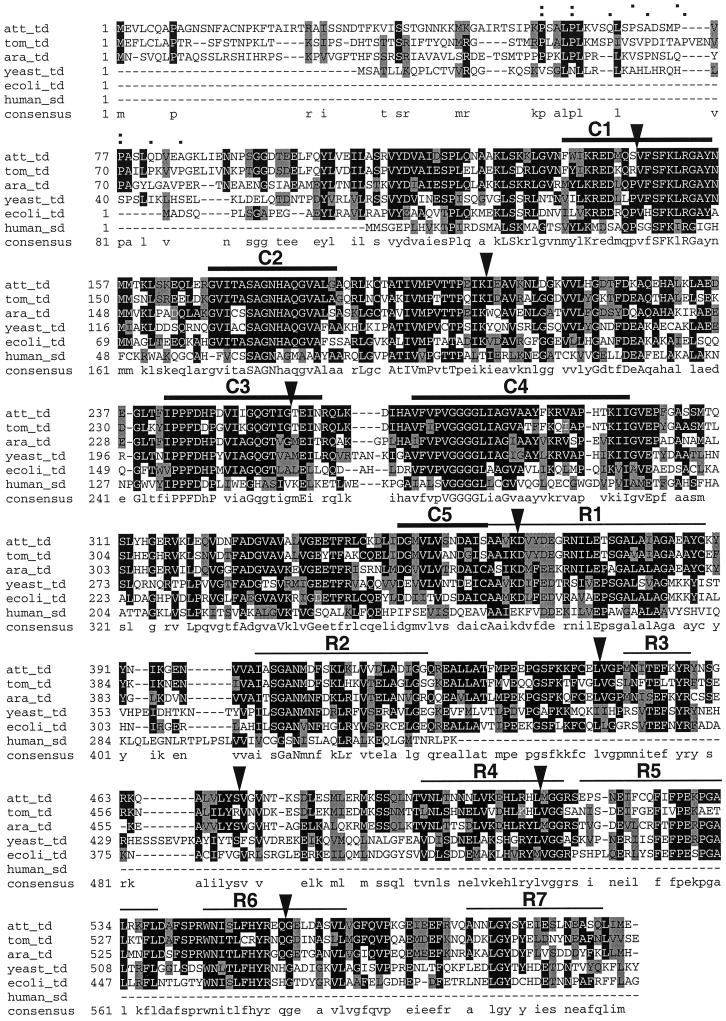
Figure 9.
Alignment of deduced amino acid sequences of TDs from N. attenuata (att_td; GenBank accession no. AF229927), tomato (tom_td; GenBank accession no. P25306), Arabidopsis (ara_td; GenBank accession no. AAF04418), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast_td; GenBank accession no. P00927), E. coli (ecoli_td; GenBank accession no. P04968), and the Ser deaminase from human (human_sd; GenBank accession no. P20132). Amino acid identity is indicated by black shading and similarity by gray shading. Uppercase letters in the consensus sequence indicate fully conserved residues, lowercase letters indicate partial conserved residues. The five catalytic domains C1 to C5 and the eight regulatory domains R1 to R7 as defined by Taillon et al. (1988) are displayed as bars. Exon-intron boundaries determined for the tomato gene by Samach et al. (1991) are indicated by triangles. Pro residues in a putative chloroplast transit peptide of N. attenuata and tomato are indicated by dots in the upper and lower row, respectively, above the alignment.