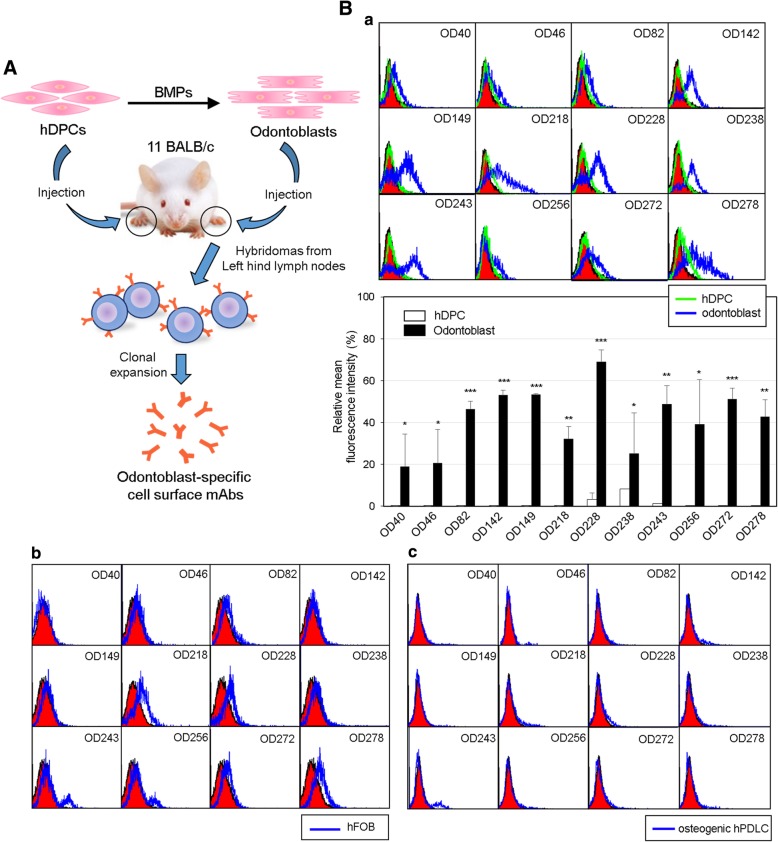
Fig. 2.
Construction of a set of monoclonal antibodies against cell surface molecules of odontoblast-like cells. A Schematic strategy of decoy immunization for construction of the odontoblast-specific cell surface antibodies. Strategy of antibody screening was described in the Materials and Methods. The intact 1 × 106 of odontoblast-like cells and hDPCs were alternatively injected into hind foot pads of 11 BALB/c mice. After immunization, the left hind lymph nodes were subjected for hybridoma construction. B Cell surface binding of 12 monoclonal antibodies on odontoblasts (a), osteoblasts (b), and osteogenic hPDLCs (c). The interaction between each antibody and cells were analyzed by immunocytometric analysis using by FACS. The filled curves indicated a negative control, which was incubated with the secondary antibody without the primary antibody. In a, black and gray curves indicated the binding on odontoblasts and hDPCs, respectively. The intensities of antibody interactions were represented as mean fluorescence. Statistics of mean fluorescence values from three independent binding tests were analyzed by Student’s t test, and asterisk indicated the significant binding difference between hDPCs and odontoblasts. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. In b, pre-osteoblastic and mature osteoblastic stages of hFOB were subjected to the incubation with the primary antibodies. Filled and open curves indicated the Ab binding on pre-osteoblasts and mature osteoblasts, respectively. In c, filled and open curves indicated the Ab binding on undifferentiated and osteogenic hPDLCs, respectively