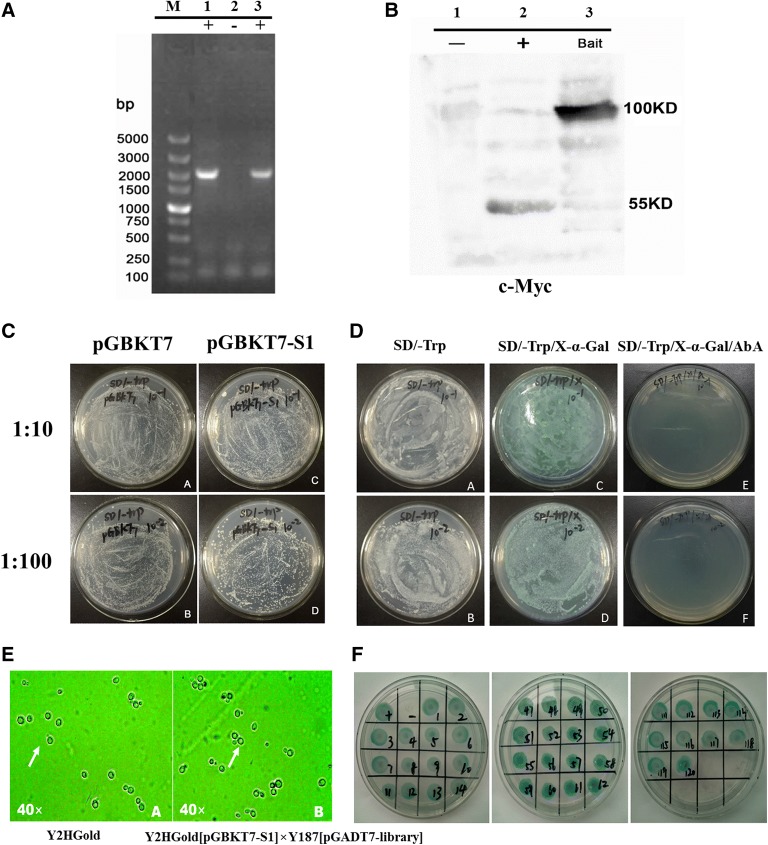
Figure 1.
Testing bait protein expression, autoactivation, and toxicity. A Yeast colony identification by PCR. M: DNA marker DL5000; 1–2: PCR of colonies transformed with pGBKT7-S1; −: blank control. B Expression of S1 in yeast by Western blotting. 1: pGBKT7 negative control; 2: pGBKT7-53 positive control; 3: pGBKT7-S1 expressed protein. C Toxicity assessment of the pGBKT7-S1 bait plasmid. Yeast cells harboring pGBKT7-S1 and the pGBKT7 control plasmid were spread at two dilutions (1:10 and 1:100) on SD/Trp plates, and the size and number of the colonies were compared to evaluate the toxicity of the bait plasmid. D Identification of autoactivation of the pGBKT7-S1 bait plasmid. Yeast cells harboring pGBKT7-S1 were spread at 1/10 and 1/100 dilutions on SD/−Trp, SD/−Trp/X-α-Gal, and SD/−Trp/X-α-Gal/AbA plates for autoactivation testing. E A yeast two-hybrid system was used to screen for S1-interacting proteins. Diploids after yeast two-hybrid screening. The zygotes typically displayed a three-lobed structure similar to a “Mickey Mouse” face at 40× magnification. F The third screen was conducted using SD/−Trp/−Leu/−Ade/−His/X-α-Gal/AbA selective medium.