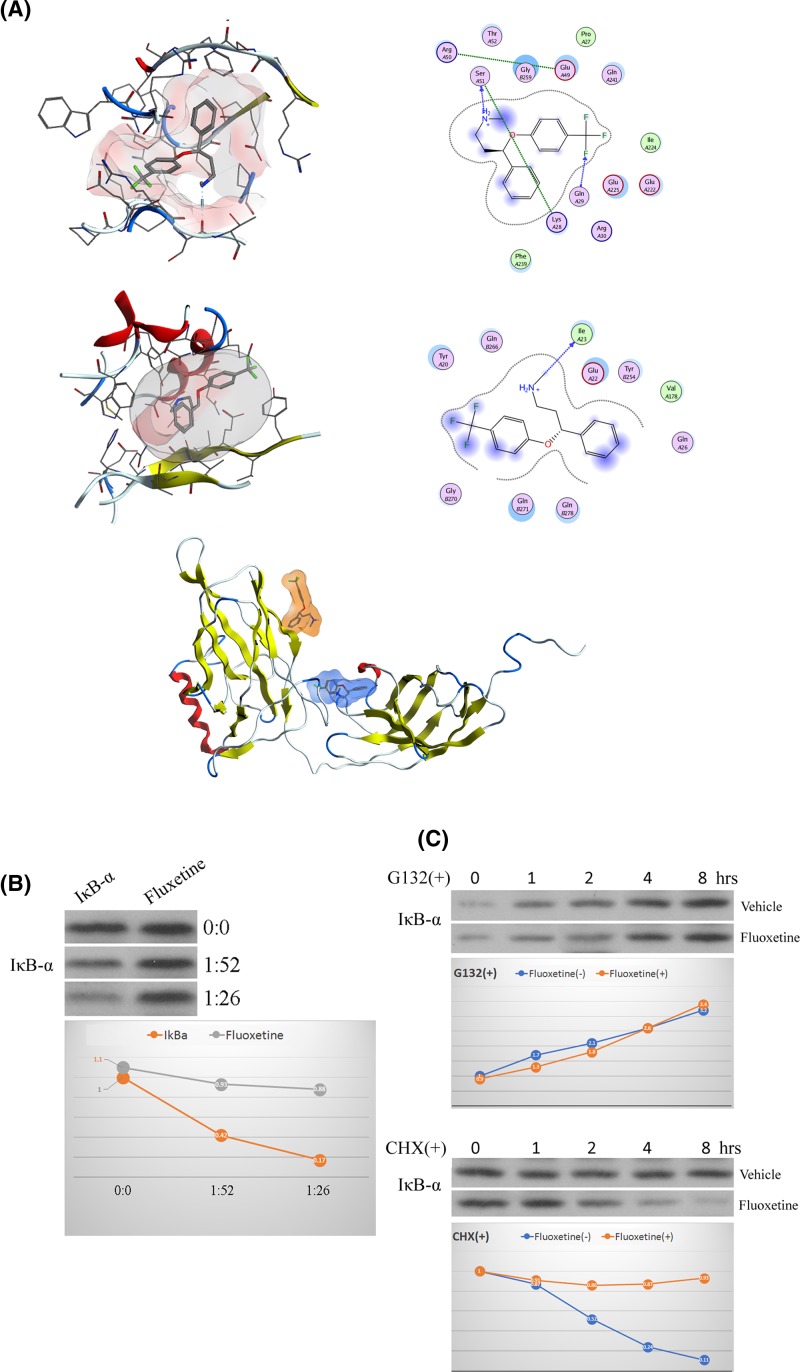
Figure 3. Effect of fluoxetine on the ubiquitylation of IκB-α in BV-2 cells.
(A) The structure of full-length IκB-α complex with fluoxetine. Top: potential binding site 1, with a binding energy of −7.3 kcal/mol, including hydrophobic and hydrogen bond interaction. Fluoxetine provided a hydrogen bond acceptor and donor with a strong hydrogen bond to ser51; middle: potential binding site 2, with a binding energy of −6.6 kcal/mol, included hydrophobic and hydrogen bond interaction. Fluoxetine provided a hydrogen bond donor; bottom: overall view of the combination of IκB-α and fluoxetine; blue, potential binding site 1; orange, potential binding site 2. (B) Detection of protein content after enzymatic hydrolysis. Left: optical density change of targetted bands in different the concentrations of pronase; right: scanned image of target bands. (C) Protein half-life detection. Left: change of IκB-α at different times with the administration of G132; right: change of IκB-α at different times with the administration of CHX.