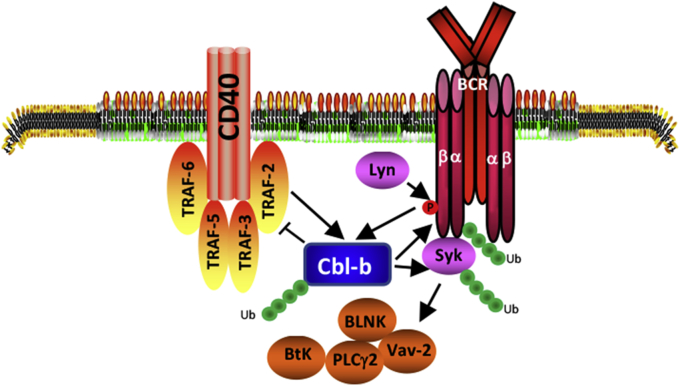
Fig. 4.
Schematic model for Cbl-b in BCR- and CD40-mediated signaling pathways Activation of CD40-dependent signaling pathway is mediated primarily by several TNFR-associated factor (TRAF) protein family members including TRAF2, 3, 5, and 6. TRAFs serve as adaptor proteins that connect the cytoplasmic domain of CD40 to downstream effector molecules, such as NF-κB, JNK and p38 MAPK. CD40 stimulation may also activate several protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) including Syk and Btk in B cells. Cbl-b inhibits the recruitment of TRAF-2 to CD40, and targets Igα, Igβ, and Syk for ubiquitination, thus inhibiting both BCR- and CD40-mediated signaling pathways. CD40 costimulation facilitates BCR-induced Cbl-b ubiquitination and degradation, thus eliminating the negative regulator Cbl-b from the BCR- and CD40-signaling pathways, and allowing optimal B cell activation to occur.