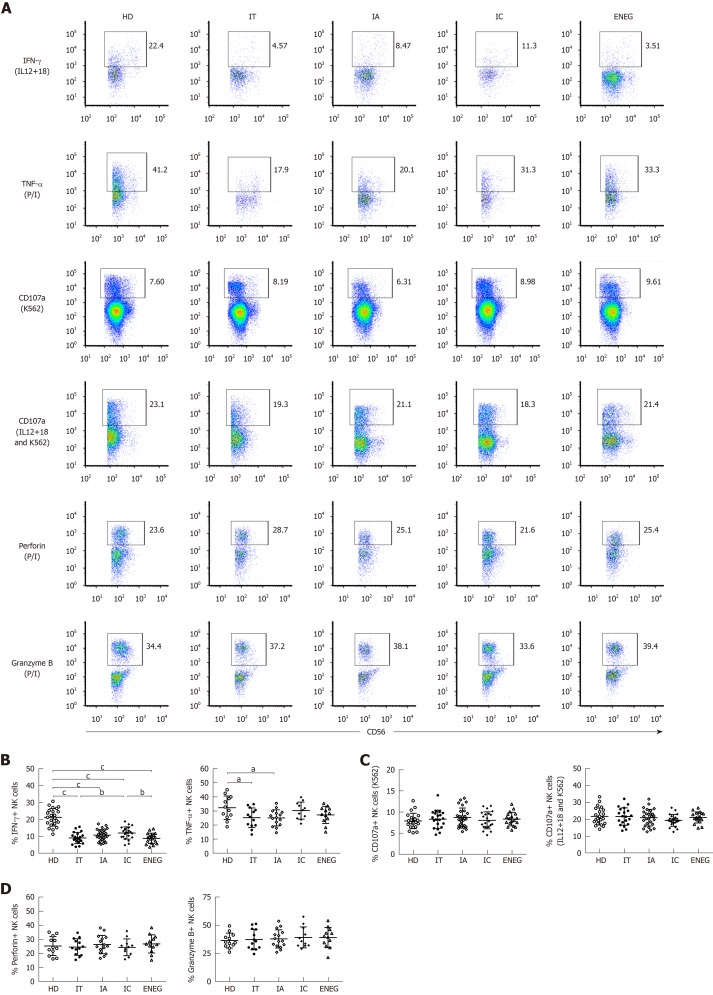
Figure 3.
NK cell functions in different clinical phases. For detecting NK cell functions, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated by IL-12 and IL-18, P/I, K562 target cells or IL-12/18 and K562 target cells. A: Gated on CD3-CD56+ NK cells, representative dot plots depicting the expression of IFN-γ, TNF-α, CD107a, perforin and granzyme B in NK cells; B: Pooled data showing the frequency of NK cells expressing IFN-γ and TNF-α at different phases; C: Pooled data showing the differences in NK cell CD107a degranulation in different phases; D: Summary data showing the frequency of NK cells producing perforin and granzyme B in different phases. IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; NK: Natural killer; HD: Healthy honors; IT: Immune tolerant; IA: Immune active; IC: Inactive carrier; ENEG: Hepatitis B envelope antigen-negative hepatitis; P/I: Phorbol myristate acetate and ionomycin. All data are presented as mean ± SD, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.