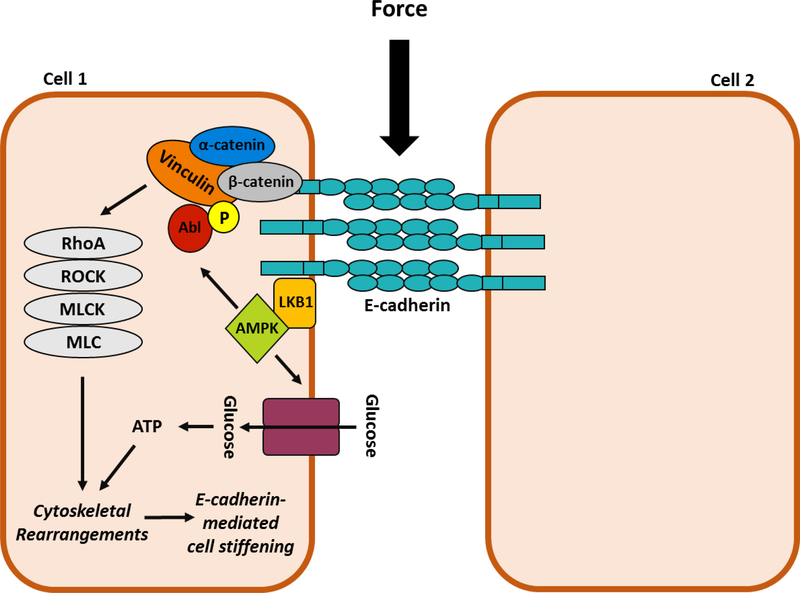
Figure 2: E-cadherin-mediated force transmission stimulates AMPK culminating in energy production.
Force on E-cadherin triggers the recruitment LKB1 and the subsequent activation of AMPK. Activate AMPK has two effects. First, it stimulates a signal transduction cascade that includes Abl-mediated phosphorylation of Y822 vinculin (yellow circle) and the subsequent activation of a RhoA-ROCK-MLCK pathway that leads to increased MLC phosphorylation and elevated contractility. Second, AMPK stimulates glucose uptake and oxidation to ATP to provide energy to allow the actin cytoskeleton to reorganized. Both signaling events are necessary for cell stiffening. LKB1=liver kinase B1; AMPK=AMP- activated protein kinase; Abl=Abelson tyrosine kinase; ROCK=Rho associated protein kinase; MLCK=myosin light chain kinase; MLC=myosin light chain.