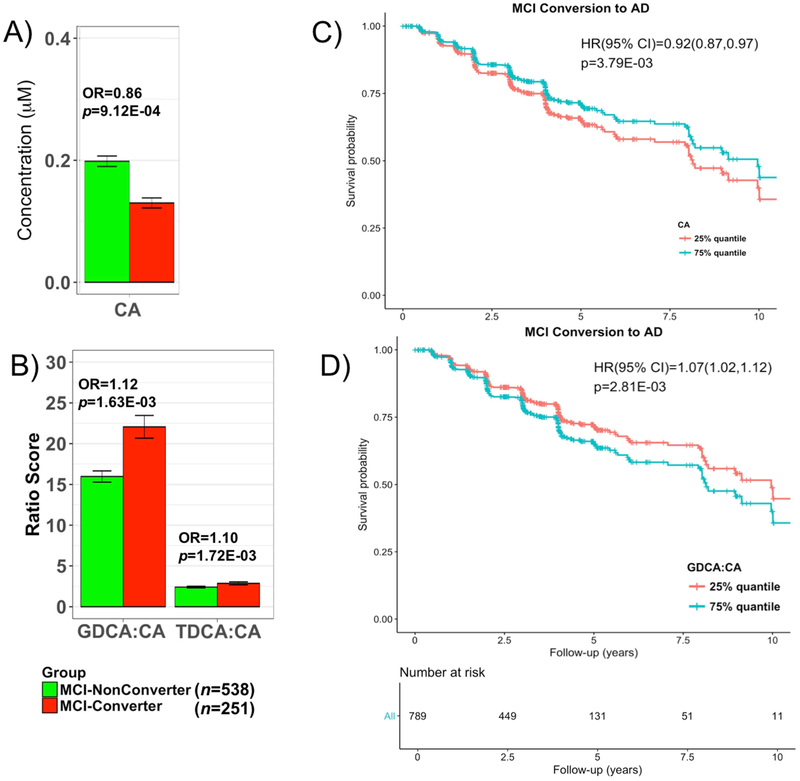
Fig. 4.
Comparison of bile levels in MCI subjects who convert and those who did not convert to AD dementia.
A and B. Lower levels of CA and higher levels of two secondary to primary ratios were significantly associated with higher odds of converting from MCI to AD. EMCI and LMCI patients that converted to AD dementia in 4 years after baseline were labeled as MCI-Converter; 9 bile acids and ratios that were significantly dysregulated between CN to AD were assessed; P-values were estimated from logistic regression models and adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, and APOE ε4 status; the significance level was adjusted for multiple testing according to Bonferroni 0.05/9 = 5.56 × 10−3. C and D. Cox hazards model of the association of conversion from MCI to AD. Red line: 1st quantile, Red line: 3rd quantile. Analysis was conducted using quantitative values and stratification by quantiles was used only for graphical representation.