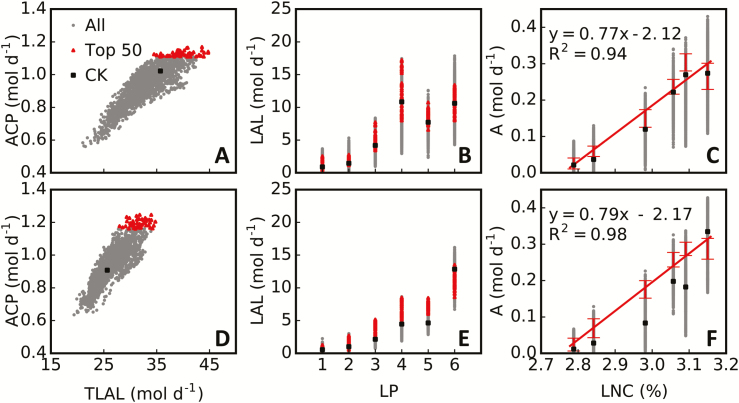
Fig. 8.
Relationships between simulated photosynthesis, light interception, and leaf nitrogen concentration. Two light conditions, strong direct light (A–C; see Fig. 6A) and strong scattered light (D–F; see Fig. 6F), were used for rice cultivar XS134 under high-nitrogen treatment. The relationships between daily total canopy leaf-accumulated absorbed light (TLAL) and daily net canopy photosynthetic CO2 uptake (ACP; A, D), between leaf position (LP; counted from bottom to top on a plant) and daily total light absorption by a leaf (LAL; B, E), and between leaf nitrogen concentration (LNC) and leaf daily total photosynthetic CO2 uptake (A; C, F) are illustrated for 2280 plant architectures (All), elite plant architectures (Top 50), and the default plant architecture (CK). ACP, TLAL, LAL, and A were calculated for 1 m2 ground area.