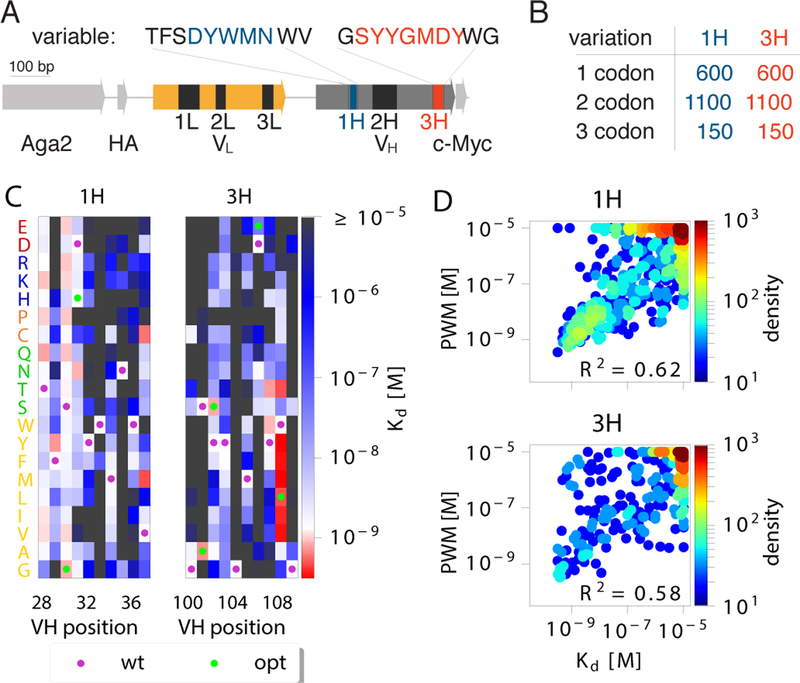
Figure 1. Additive model of binding affinity.
(A) 4–4-20 scFv antibody sequence. Six complementarity determining regions (CDR: 1L, 2L, 3L, 1H, 2H, 3H) are particularly important for antibody binding affinity. A library of antibody sequences with mutations in 10 amino-acid regions around the CDR1H and CDR3H domains were expressed using yeast display. (B) Using Tite-Seq, the binding constants Kd of all 600 single codon mutants, 1100 random double codon mutants, and 150 random triple codon mutants, were measured. (C) The Kd of single mutants for 1H and 3H domains were used to create position weight matrices (PWMs) to predict the affinity of double and triple mutants. Kd measurements were restricted to the reliable measurements interval of 10−9.5 – 10−5 M. WT sequences are marked with purple dots, optimized 4m5.3 mutations are marked in green dots. (D) Comparison between the PWM prediction and the measurement of Kd on double and triple mutants. PWM predictions outside of our reliable readout interval (10−9.5 – 10−5 M) were evaluated at the interval boundaries. The PWMs explained a significant portion of the variance, as quantified by the explained variance R2 (p < 10−61 for CDR1H, p < 10−48 for CDR3H, F-test for reduction in variance due to PWM). PWMs trained from the binding free energy, F = ln(Kd/c0), outperformed PWM trained from Kd (Fig. S3) as well as models without boundaries (Fig. S4).