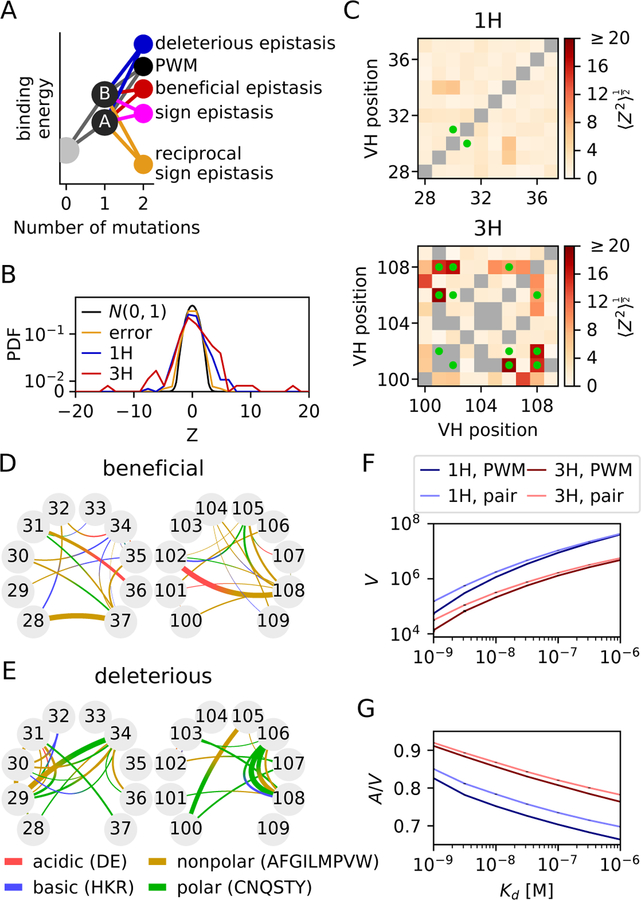
Figure 2. Quantification of epistasis.
A) Epistasis is defined as deviation from the PWM model, which assumes an additive effect of single mutations on the binding free energy F = ln(Kd/c0) expressed in units of kBT. Deleterious epistasis occurs when the measured energy exceeds the PWM prediction, beneficial epistasis occurs when the energy is less than the PWM prediction. Sign and reciprocal sign epistasis examples are shown for a beneficial interaction. (B) Distribution of Z-scores, defined as the normalized deviation from the PWM prediction, where σ2 and are the estimated errors on F and FPWM. Kd at boundaries are removed. Positive Z-scores indicate epistasis increased affinity. The Z score standard deviation was much higher than expected from measurement errors (Zerror) for CDR1H (1.78, p < 10−16, Levene’s test) and CDR3H (3.18, p < 10−48), meaning that the discrepancy between the PWM and measurement is mainly due to true epistasis. (C) Standard Z-score deviation for each pair of positions along the sequence. This deviation is higher at pairs of positions mutated in the super-optimized 4m5.3 antibody (green dots) in 3H (p = 0.005, Mann-Whitney), but not in 1H (p = 0.36). (D-E) A model of biochemical epistatic interactions between polar, nonpolar, acidic, and basic residues was fitted to the data using LASSO regularization and tested by cross-validation, yielding D) 34 beneficial and E) 32 deleterious interaction terms. Line width denotes interaction strength. (F) Number V of amino-acid sequences of the 1H (blue) and 3H (red) regions with dissociation constant below Kd, as estimated by the PWM model (dark color) or the epistatic model (light color). Epistasis enlarges the number of variants with good affinity for both 1H and 3H. (G) Mutational flux A (defined as the average number of random mutation events from all possible sequences to cause the dissociation constant to cross Kd), normalized by V, showing that epistasis also increases the accessibility of the region of good binders in sequence space. Differences between the PWM and epistatic models were robust to errors in the estimate of the interaction parameters (p < 10−5, Jackknife analysis).