Figure 4.
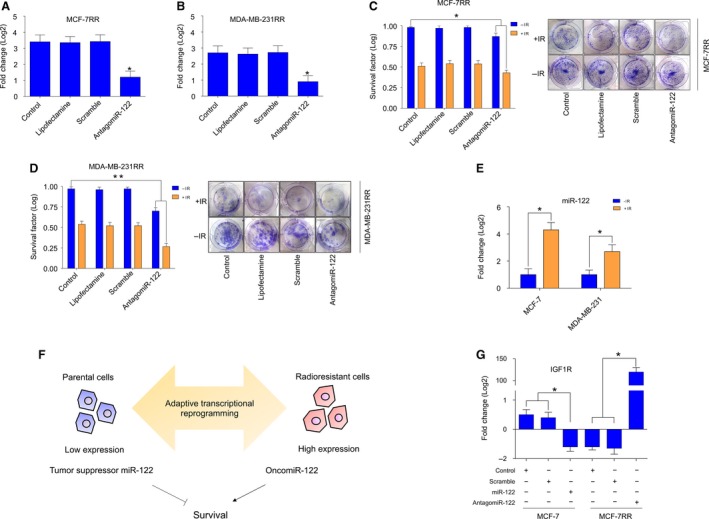
miR‐122 is overexpressed in radioresistant breast cancer cells and its inhibition reverts the radioresistant phenotype. Knockdown of miR‐122 in radioresistant (A) MCF‐7RR and (B) MDA‐MB‐231RR cells transfected with antagomiR‐122 was verified by qRT‐PCR assays. All values were normalized using RNU44 as an internal control. AntagomiR‐122‐transfected cells were evaluated for a radioresponse by clonogenic survival. Data for SF of transfected (C) MCF‐7RR and (D) MDA‐MB‐231RR cells irradiated (+IR) with 4 Gy of X‐ray are shown. Data were normalized using non‐irradiated cells (−IR). Representative images of the results of the clonogenic assays for MCF‐7RR and MDA‐MB‐231RR cells are shown in (C) and (D). (E) Overexpression of miR‐122 in parental MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 induced by treatment with 4 Gy of X‐ray was evaluated by qRT‐PCR assays. The expression data were normalized using parental MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells. All values were normalized using RNU44 as an internal control. (F) Schematic representation of the role of miR‐122 as a tumor suppressor miRNA in parental breast cancer cells and its oncogenic role during the transition from a cancer cell to a radioresistant cancer cell. (G) Expression of IGF1R in MCF‐7 and MCF‐7RR cells transfected with mimic‐miR122 and antagomiR‐122, respectively, was evaluated by qRT‐PCR. All values were normalized using GAPDH as an internal control. Data are presented graphically as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01 by ANOVA.
