Figure 1.
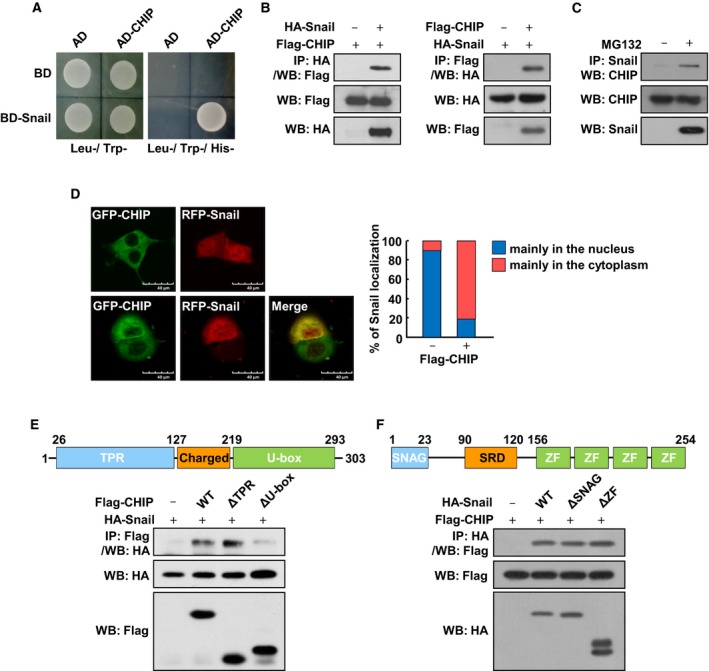
CHIP interacts with Snail. (A) Yeast two‐hybrid assays of interactions between CHIP and Snail. (B) Interaction between exogenous Snail and CHIP. HA‐Snail and Flag‐CHIP were expressed in HEK293T cells and treated with 10 μm MG132 for 6 h before harvest. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti‐HA or anti‐Flag and analyzed by western blot using anti‐Flag (left) or anti‐HA (right) antibody, respectively. (C) Interaction between endogenous Snail and CHIP. SKOV3 cells were treated with 10 μm MG132 for 6 h before harvest. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti‐Snail and analyzed by western blot using anti‐CHIP antibody. (D) Subcellular localization of CHIP and Snail. HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP‐CHIP and RFP‐Snail, respectively (upper), or cotransfected with GFP‐CHIP and RFP‐Snail (lower) and treated with 10 μm MG132 for 6 h before fixation. Cells were fixed and examined by confocal microscopy. Superimposing the two colors (merge) resulted in a yellow signal, indicating colocalization of the two proteins. Scale bars, 40 μm. The right panel presents the quantified value of the intracellular localization of Snail examined by confocal microscopy. (E) Interaction between Snail and CHIP deletion mutants. Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with HA‐tagged Snail and Flag‐tagged fragments of CHIP subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti‐Flag antibody, followed by western blot with anti‐HA antibody. (F) Interaction between CHIP and Snail deletion mutants. Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with Flag‐tagged CHIP and HA‐tagged fragments of Snail subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti‐HA antibody, followed by western blot with anti‐Flag antibody.
