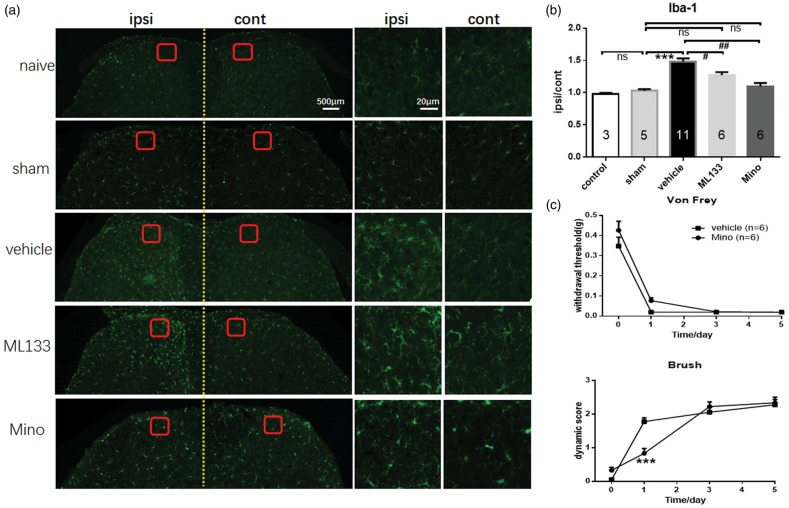
Figure 6.
Loss of brush-induced dynamic allodynia in minocycline (mino) injection mice following SNI. (a) Microglial immunostaining against Iba-1 in mice spinal cord dorsal horns after SNI surgery. (b) The histograms, respectively, show the quantification of ratio of immunostaining density on ipsilateral (ipsi) and control (cont) sides of dorsal spinal cord after SNI surgery (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc, naive vs. sham, p > 0.9999; sham vs. vehicle, p < 0.0001; vehicle vs. ML133, p = 0.0370; vehicle vs. minocycline, p = 0.0002; sham vs. mino, p > 0.9999). (c) Mino delayed the forming of dynamic allodynia following SNI (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc, p = 0.0001) while showed no significant changes on punctate allodynia (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc, p = 0.2280). Graphs represent the mean response ± SEM. ns: no significant changes; ***p < 0.001, vehicle group versus sham group in (b) and mino group versus vehicle group in (c); #p < 0.05, ML133 group versus vehicle group; ##p < 0.01, mino group versus vehicle group.