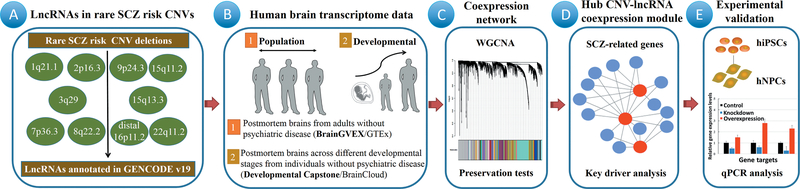
Fig. 1. Study Workflow.
We retrieved annotated lncRNAs mapped to ten SCZ risk-associated CNV deletions (A). We analyzed four human brain transcriptome data sets (BrainGVEX, Developmental Capstone, GTEx, and BrainCloud) from individuals without psychiatric disease. The BrainGVEX (N = 259) and GTEx (N = 101) data sets contained human adult control brains; the Developmental Capstone (N = 37) and BrainCloud (N = 269) data sets contained developing human brains (B). We used WGCNA to identify SCZ-related genes that were coexpressed with the CNV-lncRNAs (C). After identifying hub CNV-lncRNAs from modules related to neuronal functions (D), in vitro experiments were used to validate the predicted regulation of coexpressed SCZ-related genes by hub CNV-lncRNAs (E).