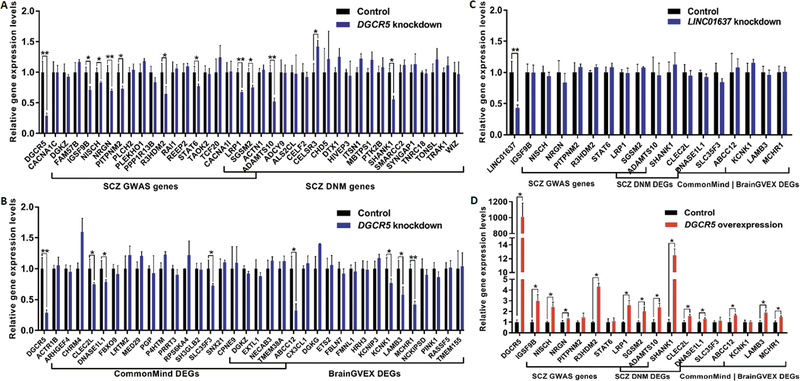
Fig. 5. DGCR5 may regulate expression of the coexpressed SCZ-related genes.
qPCR analysis was used to detect expression changes of SCZ-related genes that coexpressed with DGCR5 after DGCR5 knockdown or overexpression in hNPCs derived from hiPSCs. The blue and red bars represent the DGCR5 knockdown and overexpression groups, respectively; the black bars represent the group used as either negative control for knockdown of DGCR5 and LINC01637, or the empty vector group for overexpression. qPCR analysis was first used to detect expression changes in selected SCZ GWAS and DNM genes (A) and BrainGVEX DEGs and CommonMind DEGs (B) after knockdown of DGCR5 in hNPCs derived from hiPSCs. Positive results from (A) and (B) were further validated in experiments where the control lncRNA LINC01637 was knocked down (C) and DGCR5 was overexpressed (D) in hNPCs derived from hiPSCs. The knockdown and overexpression experiments were conducted in three biological replicates. Data are shown as means ± SEM. Gene expression in the control group was normalized to 1. Two-tailed t test was used for comparison between two groups. P values were adjusted for multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. *Padjust < 0.05, **Padjust < 0.01.