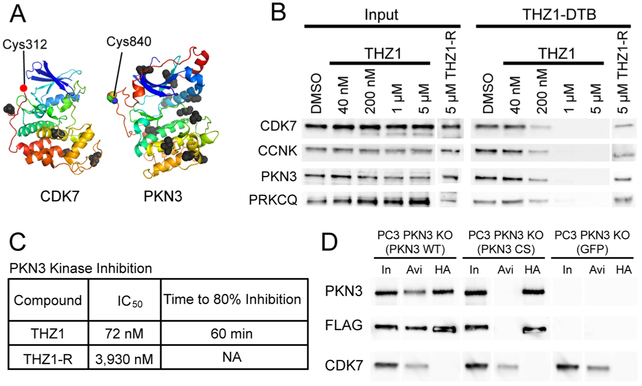
Figure 2.
THZ1 inhibits PKN3 via specific targeting of C840. (A) Structures of CDK7 and PKN3 facing kinase active sites with cysteine labeling sites of THZ1-DTB highlighted as colored spheres. All other unlabeled cysteine residues are displayed as black spheres. For CDK7, structure for Cys-312 is unavailable, a red dot indicates its approximate location adjacent to the next closest visible residue (Asp-311) (CDK7: PDB 1UA2,31 PKN3: Swiss-Model Q6P5Z2). (B) Live HeLa S3 cell treatments with THZ1 or reversible analog THZ1-R. Lysates treated with THZ1-DTB, followed by streptavidin pulldown and immunoblotting against THZ1 targets. CCNK is used as a proxy for CDK12/13. (C) Summary of PKN3 inhibition by THZ1 and THZ1-R. Middle column is IC50 values for 7-point dose–response kinase assay for PKN3. Right-most column is time-dependent kinase assays for PKN3 with fixed inhibitor concentration (1 μM). THZ1-R did not show time-dependent inhibition. See Figure S2B, C for enzyme inhibition curves. (D) C840 is essential for covalent labeling of PKN3. Dual FLAG-HA tagged PKN3 WT and PKN3 CS constructs were expressed in PC3 PKN3 KO cells. Lysates were treated with THZ1-DTB followed by streptavidin pulldown or HA immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. In = 1% Input, Avi = Streptavidin pulldown, HA = HA pulldown. Blot lanes were rearranged for clarity.