Figure 1. Oviductal telomere length (A), gene expression (B) and protein expression of DNA‐protein kinase complex components in oviducts (C). Control (open bars) v. hypoxia (grey bars).
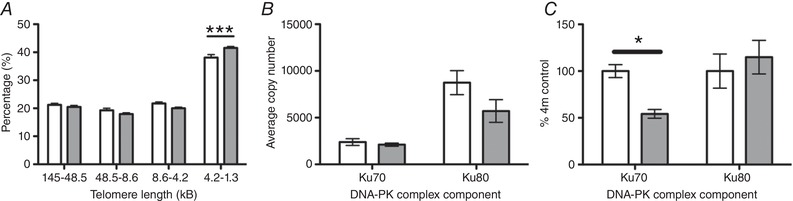
A, oviductal telomere length in adult female rats exposed to gestational hypoxia compared to normoxia. B, effect of gestational hypoxia compared to normoxia on gene expression of components (Ku70 and Ku80) of the DNA‐activated protein kinase (DNA‐PK) in the oviducts. C, effect of gestational hypoxia compared to normoxia on protein expression of KU70 and KU80. Data shown as the mean ± SEM. Open bars: normoxia (21% oxygen) during gestation, grey bars: hypoxia (13% oxygen) during gestation. * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001. n = 7–8 for all groups (n refers to the number of litters)
