Figure 8. The occlusion of KATP channels suppresses the low glucose‐induced depolarization of NTS neurons.
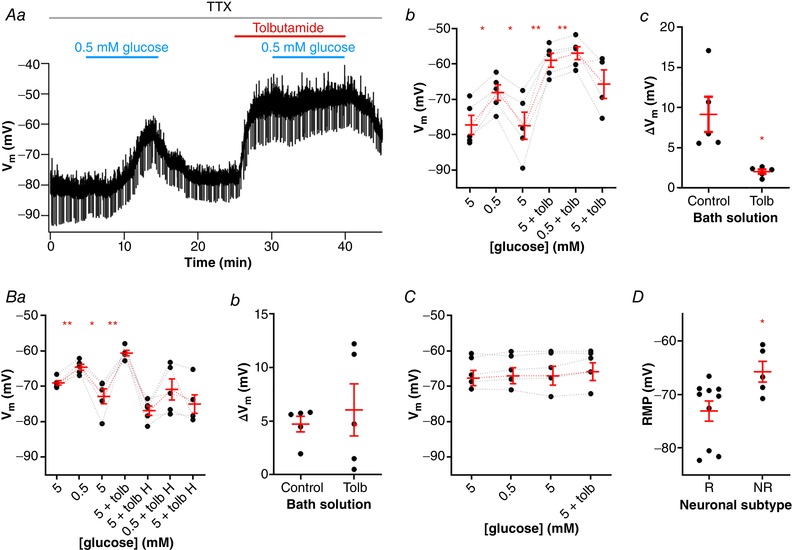
A, application of tolbutamide blunts the depolarizing effect induced by a low glucose challenge, as shown by a representative recording (Aa). Neurons responsive to low glucose are also depolarized by tolbutamide (Ab), but this effect occludes the low glucose sensing (Ac). B, hyperpolarization of neurons responsive to low glucose (Ba) prevents the effect of tolbutamide in blunting the low glucose sensing (Bb). C, neurons unresponsive to low glucose also do not respond to tolbutamide application. D, comparison of the resting membrane potential (RMP) between neurons responsive (R) and unresponsive (NR) to both low glucose and tolbutamide. H, hyperpolarization; Tolb, tolbutamide; TTX, tetrodotoxin; V m, membrane potential. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
