Figure 11. Low glucose‐induced depolarization of NTS neurons is short living and reversed by the opening of KATP channels.
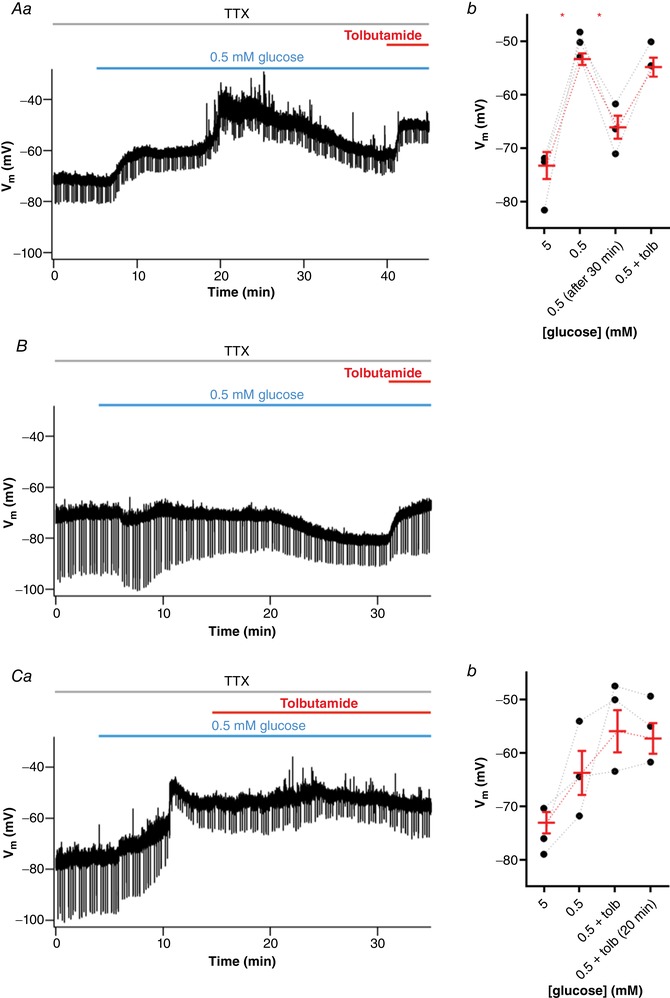
A, subset of neurons initially responsive to low glucose is hyperpolarized after a long period of exposure, as shown by a representative recording (Aa). Note that tolbutamide reverses the hyperpolarizing effect induced by low glucose. Ab, summary of the effect triggered by low glucose and tolbutamide on the membrane potential (V m) of neurons. B, a neuron non‐responsive to a low glucose challenge is hyperpolarized after more than 20 min low glucose exposure. Note that tolbutamide also reverses the hyperpolarizing effect. C, application of tolbutamide suppresses the hyperpolarization induced by a long period of low glucose perfusion, as shown by a representative recording (Ca). Cb, summary of the effect of low glucose and tolbutamide on V m of neurons. Tolb, tolbutamide; TTX, tetrodotoxin. * P < 0.05. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
