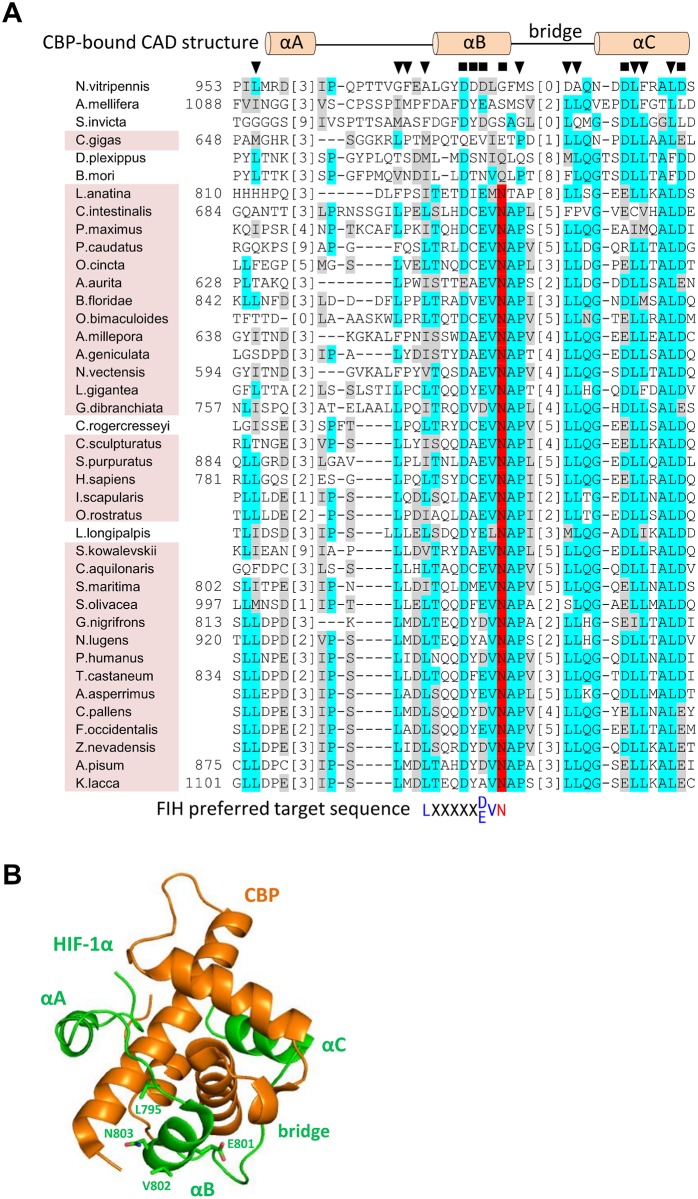
Fig 4. Conservation of CBP and FIH binding residues in HIF-α CAD homologs.
(A) Known and putative HIF-α CAD sequences from representative species were aligned using MUSCLE [50]. Identical and similar residues are indicated by cyan and grey highlights, respectively, while likely FIH target Asn residues are highlighted in red. To facilitate viewing of as large a CAD region as possible, low similarity regions of the alignment were deleted and replaced with bracketed numbers which indicate how many residues in each sequence are not shown. Amino acid numbers within the HIF-α proteins (where available) are shown to the left of the sequences. To compare functional regions of hsHIF-1α CAD with the aligned homologs, CBP and FIH-interacting residues are also depicted. Specifically, the secondary structure of hsHIF-1α CAD when bound to CBP [45] as well as residues predicted to be involved in polar (black squares) or hydrophobic (black triangles) interactions with CBP are shown above the alignment. The FIH preferred target sequence is shown below the alignment, coloured as for Fig 1. Conservation of FIH in a species is indicated by pink background shading of the species’ name, and correlates strongly with the level of sequence similarity to hsHIF-1α CAD. (B) The secondary structure depicted above the alignment in part A is shown in the context of the NMR structure of CBP (orange) bound to hsHIF-1α CAD (green) [45]. The different regions of hsHIF-1α CAD that interact with CBP, including helices αA-αC and the αB-αC bridge, and the FIH target sequence residue sidechains, Leu795, Glu801, Val802 and Asn803 are labelled with green text. Structure image generated using Pymol [Schrodinger, 2015 #1226] and PBD structure 1L8C [45].