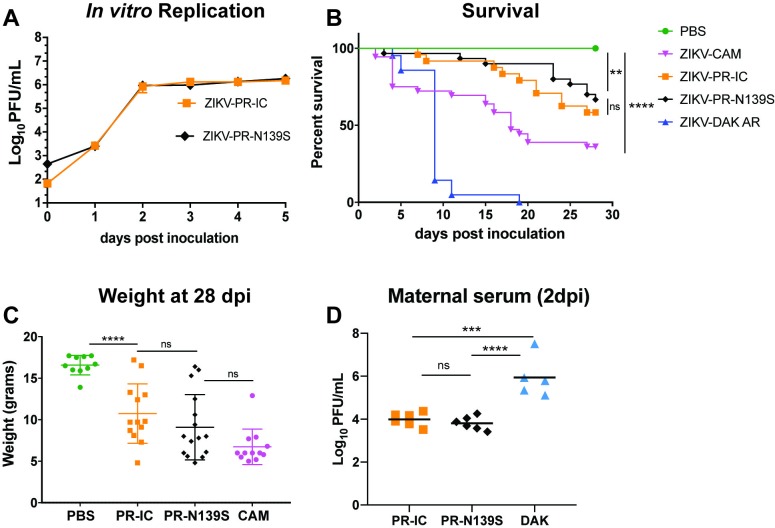
Fig 1. In vitro and in vivo characterization of ZIKV strains.
(a) In vitro growth kinetics of ZIKV-PR-IC and mutant ZIKV-PR-N139S on Vero cells. Data points represent means of three replicates at each time point ± standard deviation. Cells were inoculated at an MOI of 0.01 PFU/cell. Titer was measured (PFU/ml) by plaque assay. Growth curves were not significantly different. (b) Survival curves of neonatal BALB/c mice intracranially inoculated with 10 PFU of different strains of ZIKV. PBS: n = 18; ZIKV-CAM: n = 36; ZIKV-PR-IC: n = 24; ZIKV-PR-N139S: n = 30; ZIKV-DAK: n = 20. All strains caused significant mortality by 28 dpi when compared to PBS (Fisher’s exact test). As compared to PBS controls: ****p < 0.001; ** p <0.002; ns, not significant. (c) Weight in grams of surviving intracranially inoculated pups at 28 days post infection. ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant (student’s t-test). (d) Time-mated Ifnar1-/- dams were inoculated with 103 PFU of ZIKV on E7.5 and maternal infection was confirmed by plaque assay on day 2 post inoculation. ***p < 0.002; **** p < 0.0001; ns, not significant (one-way ANOVA).