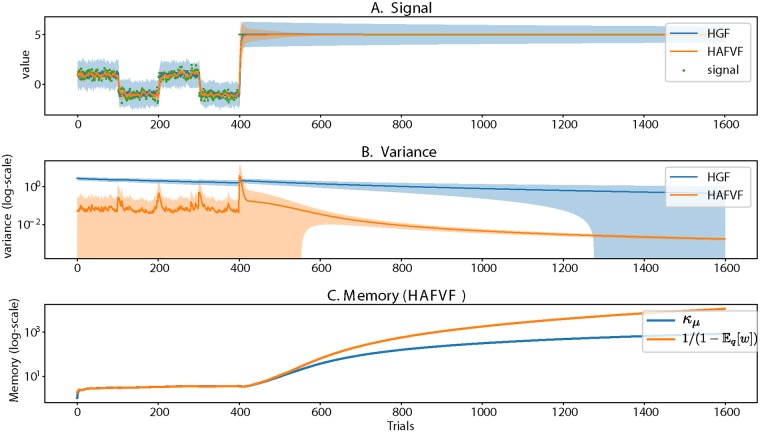
Fig 4. HAFVF and HGF performance on the same dataset.
Shaded areas represent the ±3 standard error interval. The two models were fitted to the first 400 trials, and then tested on the whole trace of observations. A. Observations, mean and standard error of the mean estimated by both models. B. The variance estimates show that the HAFVF adapted better to the variance in the first part of the experiment, reflected better the surprise at the contingency change and adapted successfully its estimate when the environment was highly stable. The HGF, on the contrary, rapidly degenerated its estimate of the variance, and did not show a significant trace of surprise when the contingency was altered. C. The value of the effective memory of the HAVFV is represented by the approximate posterior parameter κμ, and the maximum memory (efficient memory, see Bayesian Q-Learning and the problem of flexibility) allowed by the model at each trial.