Fig 6:
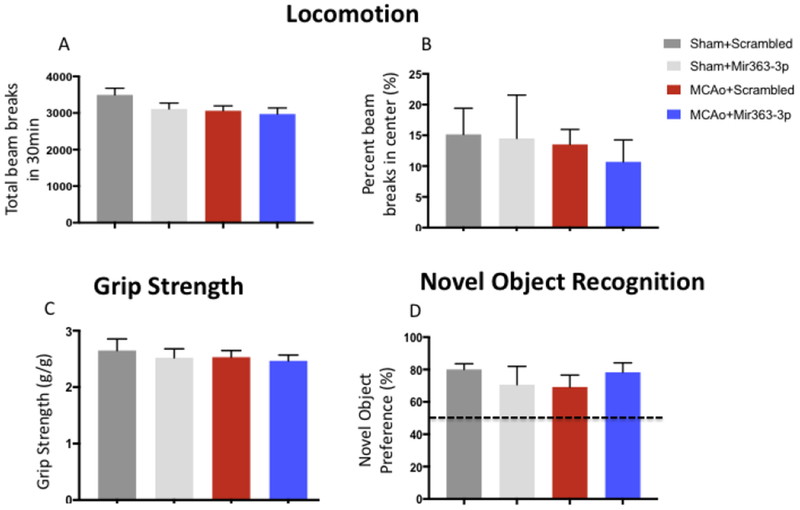
Locomotion, motor strength and cognitive changes at 3+ months (99d) after stroke: (A) Locomotor impairment was assessed by the total number of beam breaks and beam breaks in the center in an open field apparatus. (A) The total number of beam breaks was no different between sham or MCAo groups treated with either scrambled oligos or MCAo+mir363-3p at 99d after stroke. (B) The percent time spent in the center of the open field was not different in any of the groups. (C) Motor impairment was tested using the grip strength meter. The peak tension force for forelimb grip was no different between the sham or MCAo groups treated with either scrambled oligos or MCAo+mir363-3p at 99d after stroke. (D) Novel Object Recognition: Novel object recognition test was used to assess loss of cognitive capacity. All groups showed a greater preference (>50%; dotted line) for the novel object than the familiar object and were statistically no different from each other.
