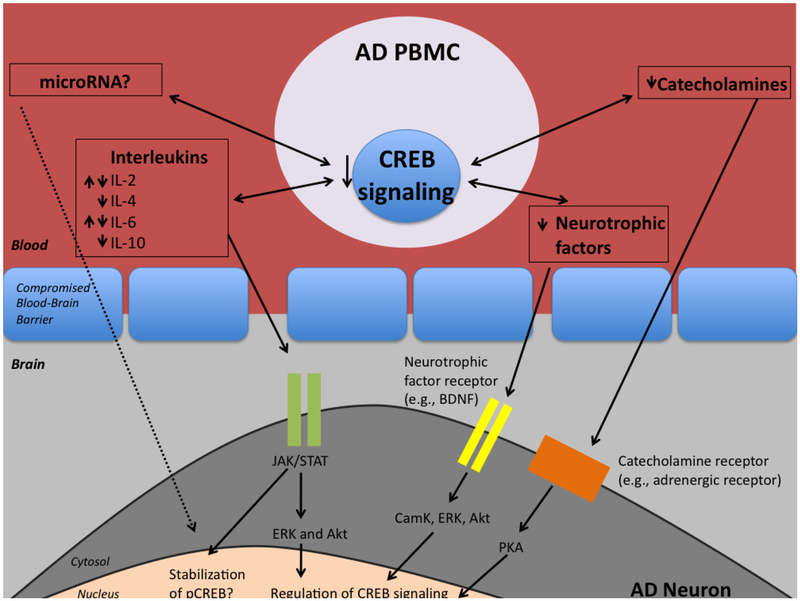
Figure 3.
Hypothesis detailing possible mechanisms by which CREB signaling in PBMC affect CREB signaling in neurons. Deficits in CREB may cause dysfunction in the production of and response to interleukins, neurotrophic factors, catecholamines, or microRNAs. These factors may traffic across the compromised blood brain barrier and signal through neuronal receptors on vulnerable neurons, thus negatively affecting CREB activation and CRE-based transcription, important for learning and memory.