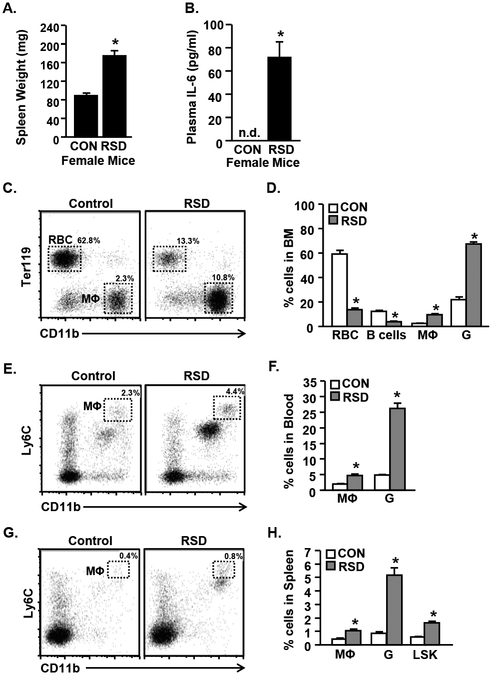
Figure 3. RSD Causes Myelopoiesis and Increases Monocyte Accumulation in the Blood and Spleen of Female Mice.
Adult female C57BL/6 mice were subjected to six cycles of modified repeated social defeat (RSD) for 30 minutes per day using a male DREADD aggressor. Spleen, bone marrow, and blood were harvested 14 h following the final cycle of social defeat and A) Spleen weight and B) plasma IL-6 levels were determined (n=6). C) Representative bivariate dot plots of CD11b and Ter119 labeling in the bone marrow are shown. D) Proportion of cells in the bone marrow including red blood cells (RBC; CD11b-/Ter119+), B-cells (CD11b-/B220+) monocytes (MΦ; Cd11b+/Ly6Chi) and granulocytes (G; CD11b+/Ly6G+). E) Representative bivariate dot plot of CD11b and Ly6C labeling in the blood. F) Proportion of monocytes (MΦ; Cd11b+/Ly6Chi) and granulocytes (G; CD11b+/Ly6G+) in blood. G) Representative bivariate dot plot of CD11b and Ly6C labeling in the spleen. H) Proportion of monocytes (MΦ; Cd11b+/Ly6Chi), granulocytes (G; CD11b+/Ly6G+), and LSK cells (Lineage-/Sca-1+/cKit+) cells in the spleen. Bars represent the mean +/− SEM. Means with asterisks (*) are significantly different than controls (p <0.05).