FIG. 7.
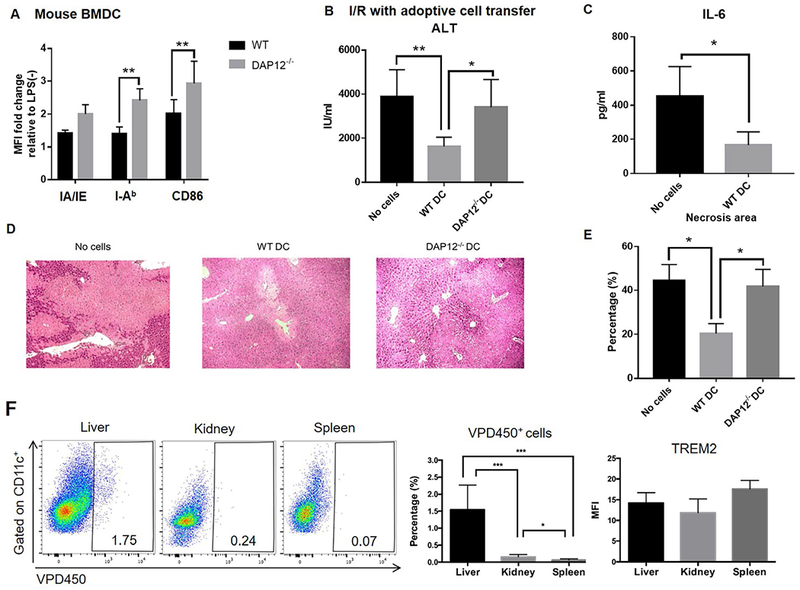
WT but not DAP12−/− DC reduce the severity of liver IRI in DAP12−/− mice. (A) Phenotype of WT or DAP12−/− DC that were infused (1-2 × 106 i.v.) into DAP12−/− mice immediately after clamp removal. (B) Serum ALT levels evaluated 6 hours after I/R. Data shown are means + SEM obtained from n = 4-12 mice per group. (C) Circulating levels of IL-6. (D) Extent of liver tissue injury observed in H&E-stained sections. (E) Quantitation of areas of necrosis. Data shown are means + SEM obtained from n = 3 mice per group. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. (F) Analysis of the in vivo migration of VPD450-labeled WT DC (infused systemically immediately after clamp removal) to the injured liver, kidney and spleen of DAP12−/− recipients performed 6 hours after I/R. Left, representative flow data from n=6 mice. Middle, aggregate data from n=6 mice denote percentages of migrated cells in the total CD11c+ population for each tissue. Right, aggregate data from n=3 mice showing the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of TREM2 staining on migrated DC in each tissue. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
