Figure 7.
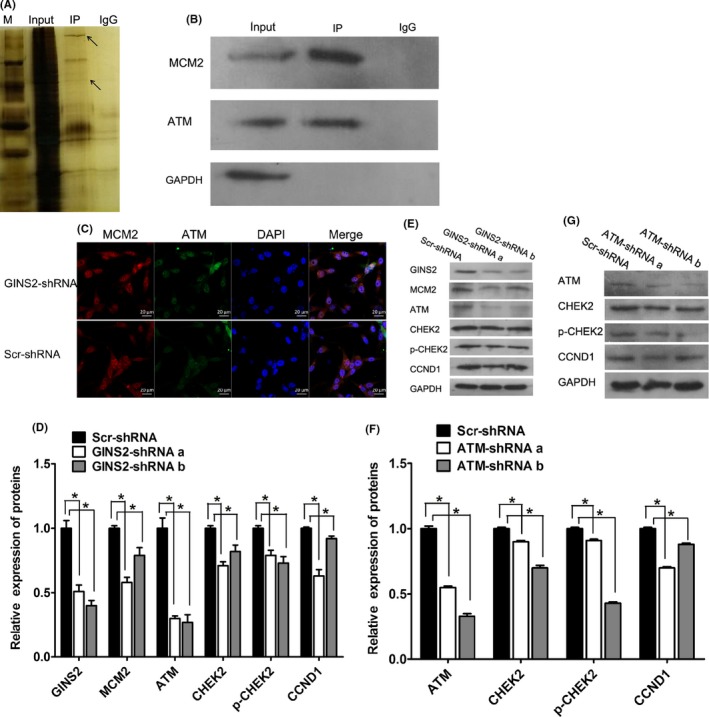
GINS2 suppression can inhibit glioma cell proliferation by regulating gene expression related to cell cycle pathways. A, B, Interaction between MCM2 and ATM by Co‐IP. A, silver staining picture. The two arrows indicate the bait protein MCM2 and the captured protein ATM; the upper arrow is ATM, and the lower one is MCM2. B, Western blot X‐ray plate. MCM2 and ATM protein levels in the Input group suggest normal expression. The detection of MCM2 protein in the IP group suggested that Co‐IP acquired MCM2, the bait protein, and the detection of ATM indicated the interaction between ATM and MCM2. C, IF double standard experiment. Red fluorescence is ATM; green fluorescence is MCM2; blue is the DAPI counterstaining. Confocal laser scanning microscope, CLSM. D, E, After suppressing GINS2 expression in human U87 glioma cells, the protein levels of MCM2, CHEK2, p‐CHEK2, CCND1, etc, declined, as shown by WB analysis. F, G, After suppressing ATM expression in human U87 glioma cells, the protein levels of CHEK2, p‐CHEK2, CCND1, etc, declined by WB analysis. The results represent mean ± SD of three separate experiments (*P < 0.05)
