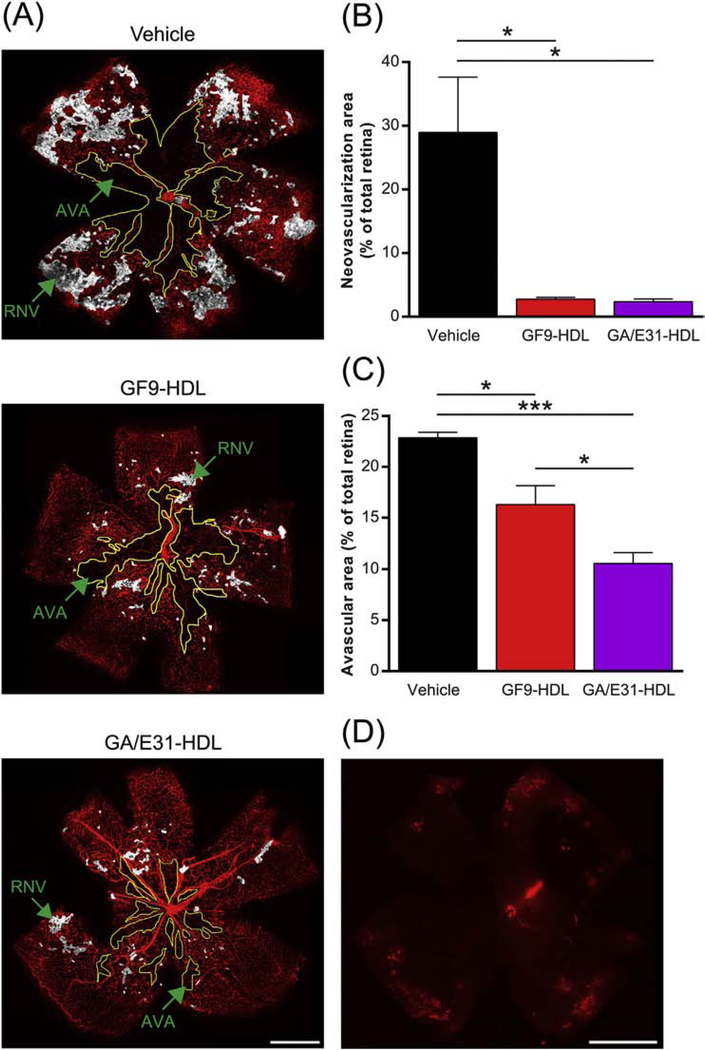
Fig. 4.
TREM-1 blockade reduces pathological retinal neovascularization and avascular areas in OIR. As described in the methods, OIR mice were treated by daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of GF9-HDL (2.5 mg/kg), GA/E31-HDL (4 mg/kg) or vehicle (PBS) from P7 to P17. (A) Representative retina flat-mounts at P17 stained using isolectin B4 (red) from the indicated treatment groups. Regions of retinal neovascularization (RNV) and avascular areas (AVA) are indicated. Scale bar = 500 μm. (B) Quantification of RNV. Data were analyzed from 3 independent experiments (n = 6 retinas, 3 litters of mice) and represented as the mean ± SEM. *, p < 0.05. (C) Quantification of AVA. Data were analyzed from 3 independent experiments (n = 6 retinas, 3 litters of mice) and represented as the mean ± SEM. *, p < 0.05, ***, p < 0.001. (D) IFA of a representative retina flat-mount confirms that systemically (i.p.) administered rhodamine B-labeled GF9-HDL penetrate the blood-retinal barrier and accumulate in the retina, delivering their payload (similar for GA/GE31-HDL, as shown in Supplemental Fig. 1C). Scale bar = 500 μm.