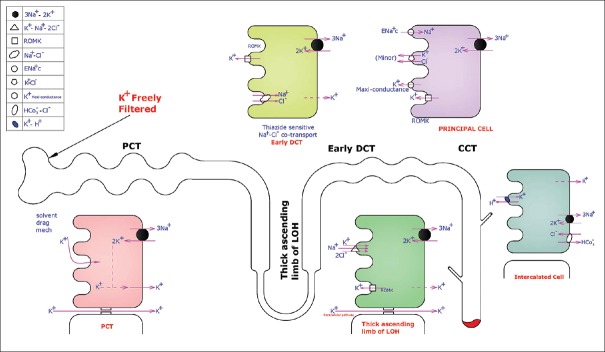
Figure 2.
This figure shows K+ handling by the kidney. Proximal convoluted tubule: 65% K+ is reabsorbed. Thick ascending loop of Henle: K+ enters the cell via the Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter. Early distal convoluted tubule: Na+ and Cl− reabsorbed by Na+–Cl− cotransporter. K+ is secreted into the lumen via the renal outer medullary potassium channel. Late distal convoluted tubule, connecting tubule, and cortical collecting duct: (1) Principal cells: K+ secreted into the lumen by the renal outer medullary potassium channels and K+ maxi conductance channels. Epithelial Na channel shifts Na from the lumen to inside the cell. (2) Intercalated cells Type A: K+ taken up inside the cell from the lumen with the help of K+–H+ exchanger