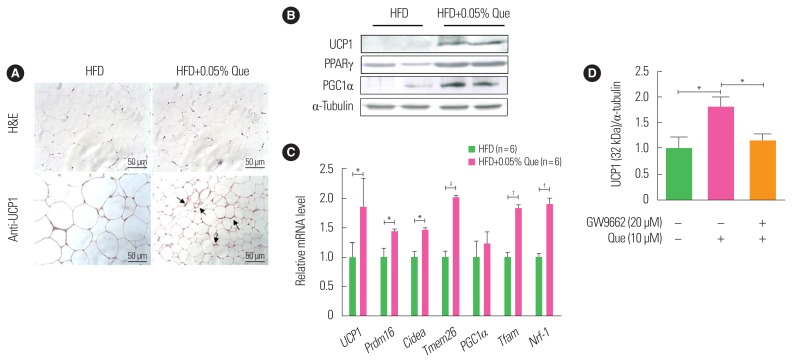
Figure 1.
Dietary quercetin enhances expression of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) and thermogenic genes in white adipose tissue (WAT). C57BL/6 mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) without or with 0.05% quercetin (HFD or HFD+Que) for 9 weeks. (A) Sections obtained from WAT (inguinal adipose tissue) were stained with H&E and an anti-UCP1 antibody. Original magnification, ×200. The arrows indicate increased UCP1 staining. (B) A representative Western blot showing protein expression levels of UCP1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), and PPARγ coactivator 1-alpha (PGC1α) in inguinal adipose tissue. (C) Expression of thermogenic markers and mitochondrial biogenesis markers were measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Results are mean±standard error of the mean (SEM; n=6 mice per group). *P<0.05; †P<0.01; ‡P<0.001 compared with control obese mice. (D) 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with or without quercetin and/or GW9662 (PPARγ antagonist). Results are mean±SEM of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared with control.