Figure 2.
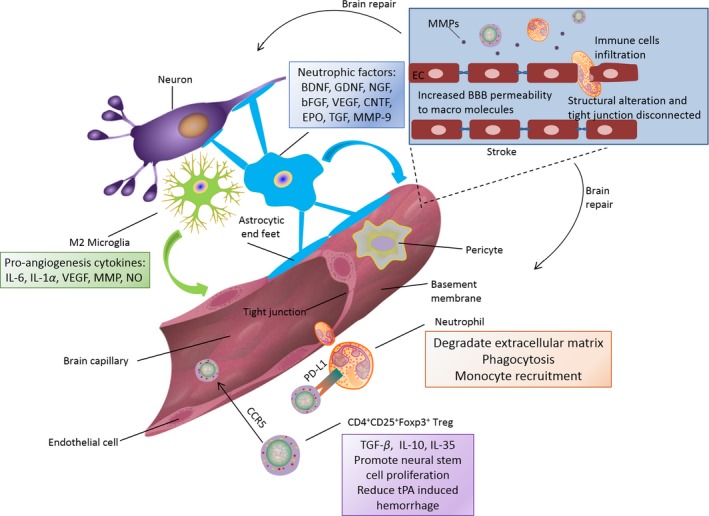
Neurovascular unit remodeling after stroke. Microglia in M2 phenotype can generate proangiogenesis factors such as IL‐6, interleukin‐1α, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and nitric oxide. In chronic phase of stroke, astrocytes can promote neuronal survival and neurovascular unit remodeling by producing brain‐derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), gliaderived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), erythropoietin (EPO), transforming growth factors (TGF) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9). Neutrophils assist neurovascular unit repair through extracellular matrix degradation, phagocytosis, monocyte recruitment. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs can release anti‐inflammatory cytokines of TGF‐β, IL‐10 and IL‐35. They can also promote neural stem cell proliferation and reduce tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)‐induced haemorrhage. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs can be recruited to ischemic blood brain barrier by CCR5 and alleviate BBB disruption through the expression of PD‐L1
