Figure 2.
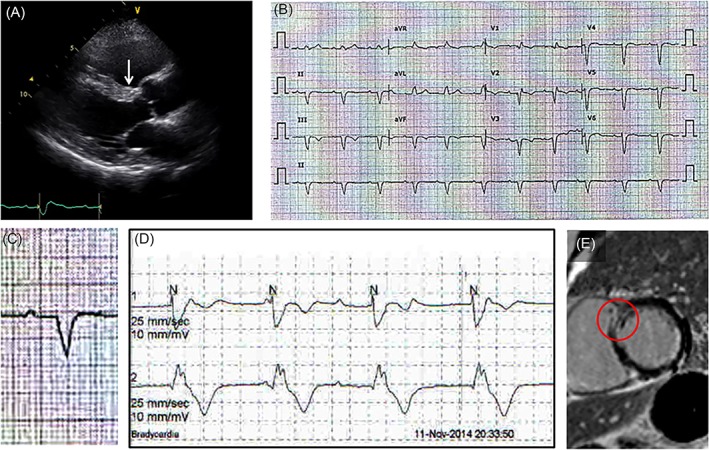
Clinical usefulness of resting EKG finding. A, Wall motion abnormality at the basal anterior septum (arrow) was not apparent. Only high echogenicity compared with the rest of the anterior septum is noted. B and C, Resting EKG showing first‐degree AV block with a wide QRS complex. As a cause of PR prolongation, the possibility of a tri‐fascicular block should be considered. D, Holter monitor showing intermitted complete AV block with wide QRS escape beats suggesting an infra‐His block. Therefore, it is not relevant to think that a first‐degree AV block as a conduction delay at the AV node and an infra‐His AV block exist separately. E, EKG findings in this patient suggest that a certain pathologic lesion is most likely present at the basal anterior septum (arrow in A). Therefore, even the tiny mid‐wall delayed enhancement at the basal anterior septum shown here, otherwise neglected, should be considered as a pathologic delayed enhancement. AV, atriventricular; EKG, electrocardiogram; PR, PR interval; QRS, QRS complex
