Figure 5.
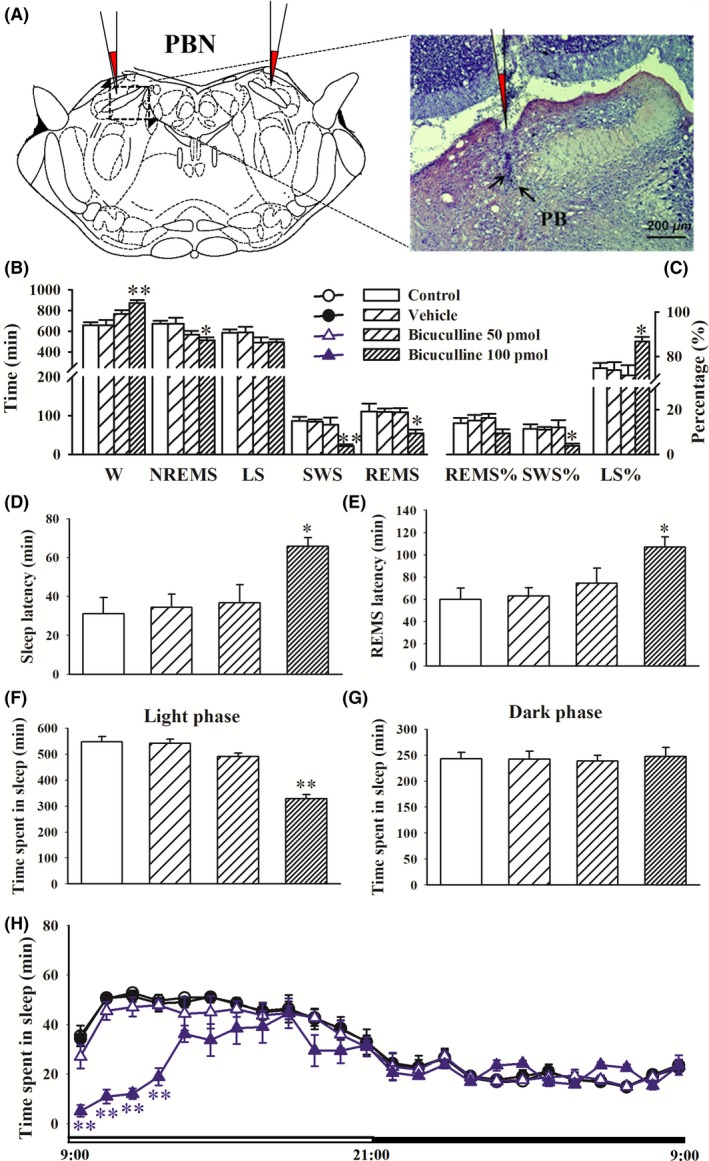
Microinjection of bicuculline in the PBN promoted wakefulness and decreased sleep. Sleep recording was performed 24 h immediately after vehicle or bicuculline (50 or 100 pmol/side) intra‐PBN application. A, Schematic representation of the cannula implantation sites 1 mm above the PBN and bright‐field photomicrograph of a coronal brain section showing the injector tip (black arrowhead). B‐E, Time spent in wakefulness (W), rapid eye movement sleep (REMS), nonrapid eye movement sleep (NREMS), and slow‐wave sleep (SWS) per 1 h. F, G, Sleep latency and REM sleep latency. H, Time spent in sleep per 1 h. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 8‐11 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs vehicle group (Student‐Newman‐Keuls test)
