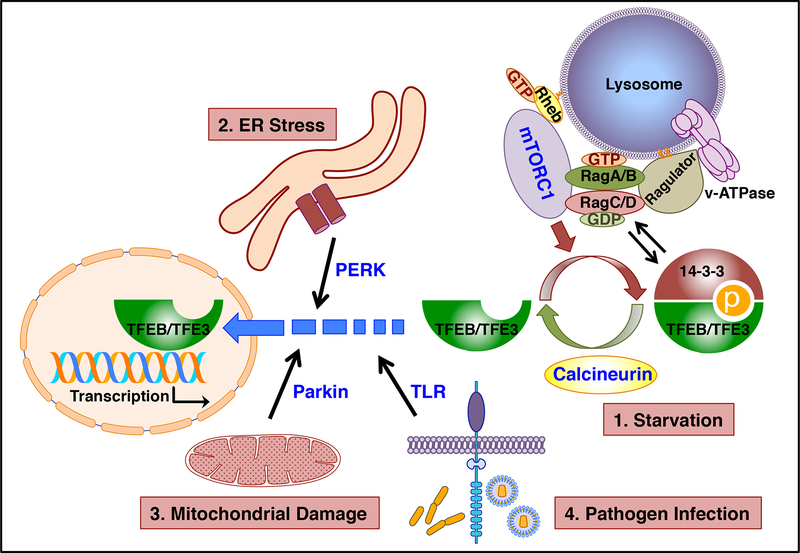
Figure 1. TFEB/TFE3 respond to different types of cellular stress.
Under normal conditions mTORC1 phosphorylates TFEB/TFE3, thus promoting their cytosolic retention. Following starvation (1), mTORC1 inactivation together with activation of specific phosphatases such as calcineurin, lead to TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation. TFEB/TFE3 activation is also observed in response to ER stress (2), mitochondrial damage (3), and pathogen infection (4). The proteins implicated in TFEB/TFE3 activation under different stress conditions are represented in blue.