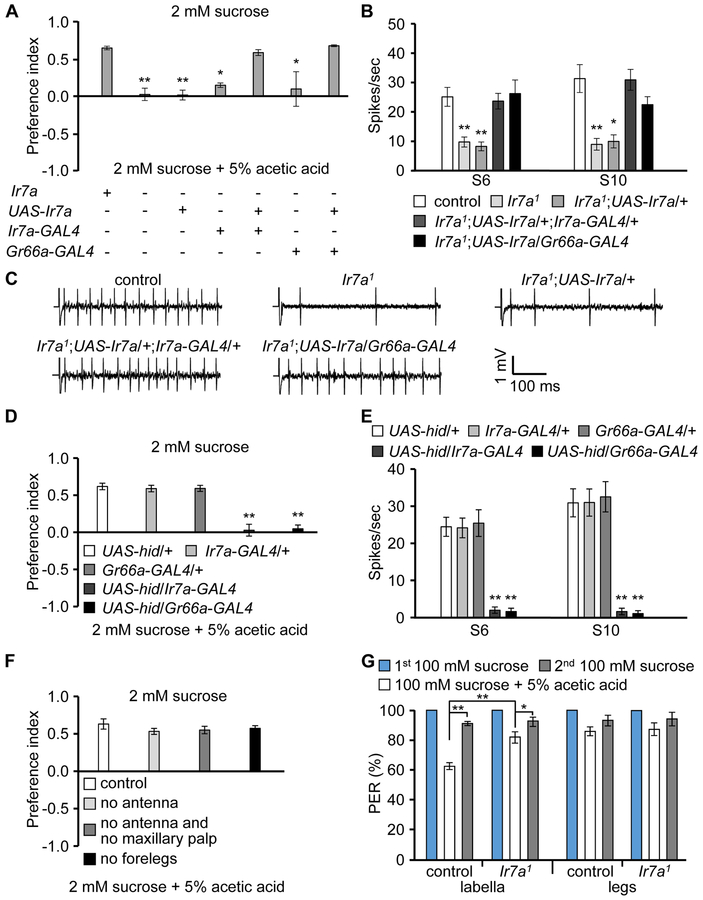
Figure 4. Ir7a is necessary for acetic acid detection in bitter-sensing GRNs in the labellum.
(A) Two-way choice feeding assays showing rescue of the avoidance defect in Ir7a1 in response to acetic acid. n=4-6.
(B) Rescue of the Ir7a1 defect in neuronal firing in response to 1% acetic acid by expression of Ir7a in either Ir7a- or Gr66a-positive GRNs. n=10-12.
(C) Representative traces obtained from S10 sensilla in response to 1% acetic acid.
(D) Two-way food choice assays after expressing the cell death gene, hid (UAS-hid), under control of the Ir7a-GAL4 or the Gr66a-GAL4. n=6.
(E) Average frequency of action potentials elicited after expressing UAS-hid under control of the Ir7a-GAL4 or the Gr66a-GAL4. n=11-13.
(F) Two-way choice feeding assays after removing the indicated organs. n=4-6.
(G) Average percentages of flies extending their proboscis after applying the indicated stimuli to labella or legs. The 1st and 2nd 100 mM sucrose refers to application of sucrose before and after application of 100 mM sucrose + 5% acetic acid. n=4-6.