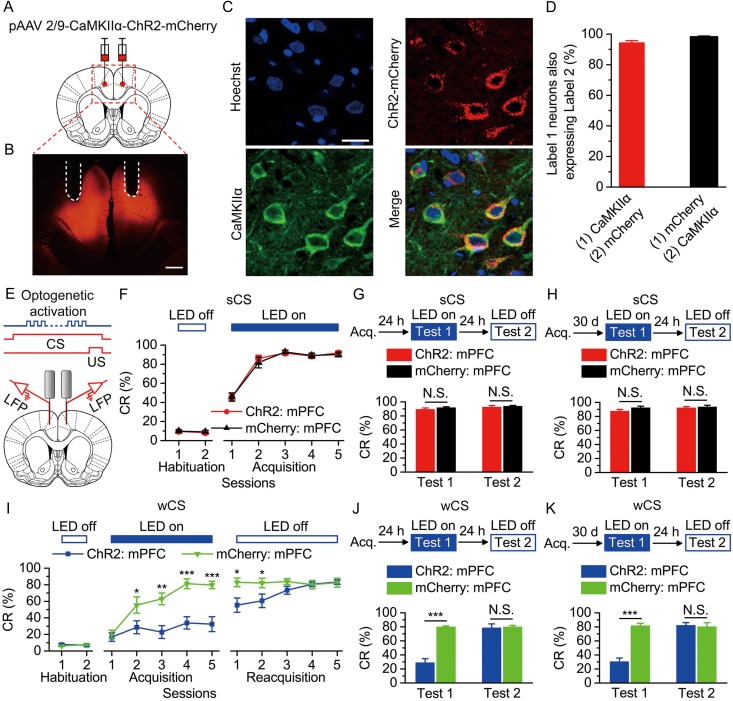
Figure 3.
Optogenetic activation of the bilateral caudal mPFC impaired the acquisition, recent and remote retrieval of DEC with the wCS, but not of DEC with the sCS. (A) Rats were injected with pAAV 2/9-CaMKIIα-ChR2-mCherry or pAAV 2/9-CaMKIIα-mCherry targeting the bilateral caudal mPFC. (B) Example of ChR2-mCherry expression in the bilateral caudal mPFC. White dashed line: optrode position. Scale bar, 500 μm. (C) Representative images showing cell-specific ChR2-mCherry expression (red) in pyramidal neurons (green) in mPFC. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Statistics of expression in pyramidal neurons (497 cells, from 5 rats). (E) Scheme for optical fiber implant site and 470-nm LED illumination pattern to bilateral caudal mPFC during each trial. (F–K) Top: Training and illumination phase protocol. Bottom: Effects of mPFC optogenetic activation during each trial on CR% of acquisition (F: n = 12 each; I: n = 12 ChR2: mPFC, n = 11 mCherry: mPFC), recent retrieval (G: n = 11 each; J: n = 12 ChR2: mPFC, n = 9 for mCherry: mPFC), and remote retrieval (H: n = 11 each; K: n = 12 ChR2: mPFC, n = 11 mCherry: mPFC) of DEC with the sCS or wCS (N.S., not significant, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; 2-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Tukey post hoc test or 2-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m.