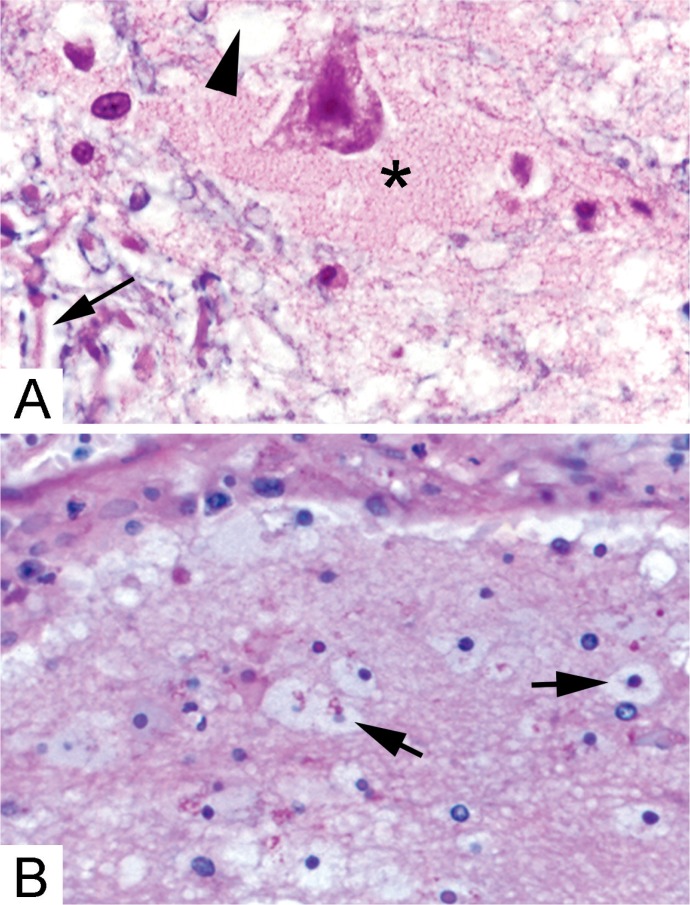
Image 3:
Histologic features of brain edema. A) Near sites of hemorrhage or blood-brain barrier disruption, plasma proteins fill the expanded extracellular space surrounding neurons (*). Intracellular edema can manifest as empty appearing glial cell cytoplasm (arrowhead) or separation of myelin (blue) from the surrounding axons (arrow) (Solochrome cyanin & eosin, x400). B) Plasma proteins are ingested by astrocytes and oligodendrocytes leading to a swollen, eosinophilic appearance (arrows) (H&E, x200).