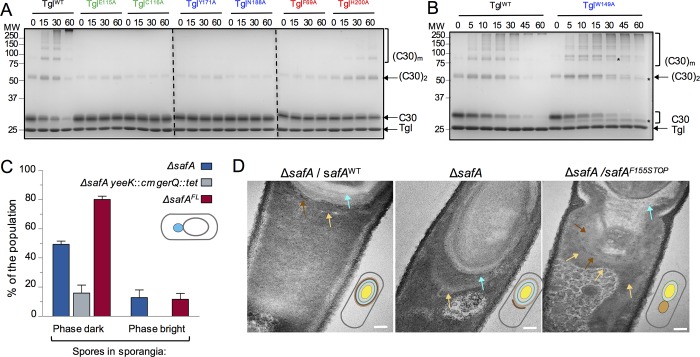
Fig 5. Non-catalytic residues, important for the localization of Tgl are also important for the cross-linking of C30 in vitro.
C30 and Tgl (either TglWT or the indicated mutant forms in A and B) were incubated at 37°C, and samples were collected at the indicated times (in min). The gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue for protein visualization; Tgl and the different forms of C30 are identified on the right-hand side of each panel. (C30)2 corresponds to a possible dimer of C30, while (C30)m represents multimeric forms of C30. The asterisks in panel B indicate the site of migration of forms of C30 that are only detected in assays with TglW149A. Enzymes are color coded according to the location of the residues exchanged relative to the tunnel of Tgl: green, catalytic residues; blue, front side of the tunnel; red, back side of the tunnel. The site of migration of the molecular weight markers, in kDa, is indicated on the left side of each panel. C: Production of C30 in the absence of SafAFL causes mislocalization of Tgl-CFP. Tgl-CFP was produced in the indicated strains and the percentage of sporangia in which the fusion protein localized as a single dot of fluorescence on the MCP pole of the forespore (schematically represented on the right side) was scored. Only strains where this pattern of localization was observed are illustrated. Note that the ΔsafAFL mutant bears the safAF155STOP allele, and only produces C30 (see text for details). The mean and standard deviation are represented. D: Samples were collected from sporulating cultures of the indicated strains 6 hours after the onset of the process and analyzed by thin sectioning TEM. Note that the ΔsafA allele was complemented at amyE with either safAwt or safAF155STOP. The blue arrows points to the cortex region, the brown arrows to inner coat material and the yellow arrows to the position of outer coat material. Scale bar, 100 nm.