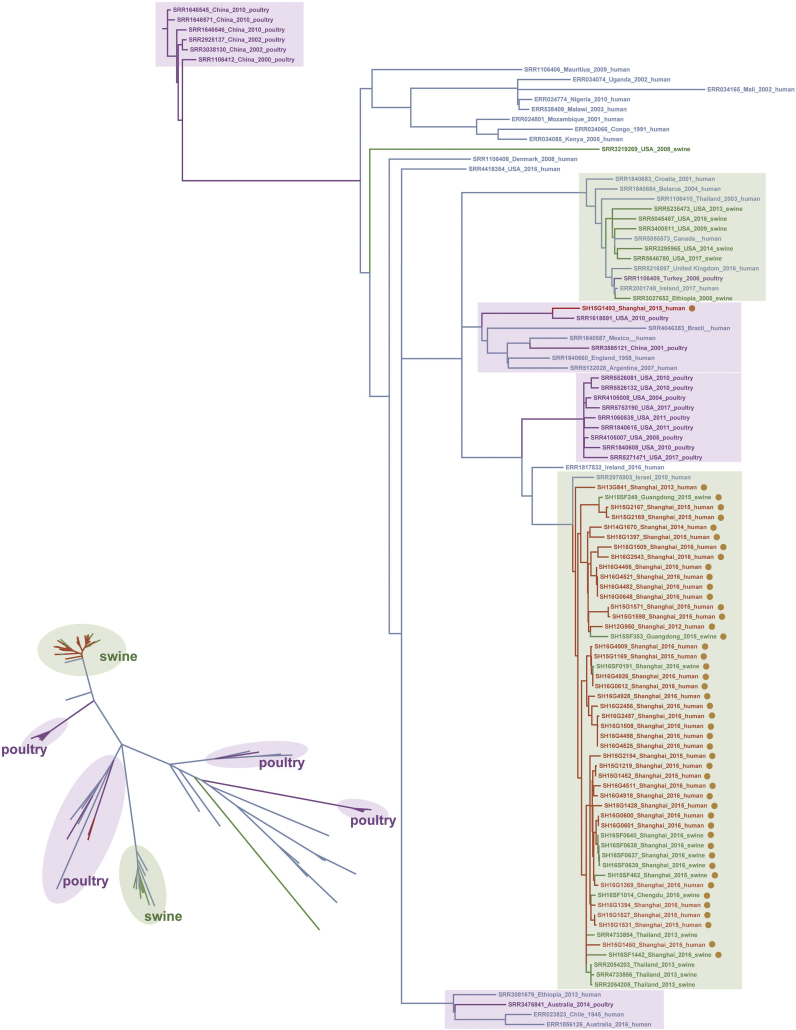
Fig. 7.
Dendrograms of mcr-1-positive S. Typhimurium isolates from different hosts. In addition to the 35 mcr-1-harbouring S. Typhimurium strains from humans found in this study, another 10 mcr-1-positive S. Typhimurium strains from swine obtained by our team and 55 mcr-1-negative S. Typhimurium genomic sequences retrieved from GenBank (comprised of 19 from poultry, 11 from swine, and 25 from humans) were also included in this analysis. Red: mcr-1-harbouring S. Typhimurium strains isolated from humans; Green: S. Typhimurium strains isolated from swine; Purple: S. Typhimurium strains isolated from poultry; Blue: mcr-1-negative S. Typhimurium strains isolated from humans. Right phylogenetic tree: the strains carrying mcr-1 plasmids are marked with light-brown spots, the branches containing swine-source strains are marked with light green boxes as the background, and the branches containing poultry-source strains are marked with light purple boxes. Bottom-left phylogenetic tree: the branches containing strains from different sources are marked with the same colour format as the phylogenetic tree on the right, to more clearly present the separation of the branches and locations of the mcr-1-harbouring strains. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)